Sticky Postings
By fabric | ch
-----
As we continue to lack a decent search engine on this blog and as we don't use a "tag cloud" ... This post could help navigate through the updated content on | rblg (as of 09.2023), via all its tags!
FIND BELOW ALL THE TAGS THAT CAN BE USED TO NAVIGATE IN THE CONTENTS OF | RBLG BLOG:
(to be seen just below if you're navigating on the blog's html pages or here for rss readers)
--
Note that we had to hit the "pause" button on our reblogging activities a while ago (mainly because we ran out of time, but also because we received complaints from a major image stock company about some images that were displayed on | rblg, an activity that we felt was still "fair use" - we've never made any money or advertised on this site).
Nevertheless, we continue to publish from time to time information on the activities of fabric | ch, or content directly related to its work (documentation).
Thursday, October 26. 2017
Note: following my previous post about Google further entering the public and "common" space sphere with its company Sidewalks, with the goal to merchandize it necessarily, comes this interesting MIT book about the changing nature of public space: Public Space? Lost & Found.
I like to believe that we tried on our side to address this question of public space - mediated and somehow "franchised" by technology - through many of our past works at fabric | ch. We even tried with our limited means to articulate or bring scaled answers to these questions...
I'm thinking here about works like Paranoid Shelter, I-Weather as Deep Space Public Lighting, Public Platform of Future Past, Heterochrony, Arctic Opening, and some others. Even with tools like Datadroppers or spaces/environments delivred in the form of data, like Deterritorialized Living.
But the book further develop the question and the field of view, with several essays and proposals by artists and architects.
Via Abitare
-----
Does public space still exist?
Gediminas Urbonas, Ann Lui and Lucas Freeman are the editors of a book that presents a wide range of intellectual reflections and artistic experimentations centred around the concept of public space. The title of the volume, Public Space? Lost and Found, immediately places the reader in a doubtful state: nothing should be taken for granted or as certain, given that we are asking ourselves if, in fact, public space still exists.
This question was originally the basis for a symposium and an exhibition hosted by MIT in 2014, as part of the work of ACT, the acronym for the Art, Culture and Technology programme. Contained within the incredibly well-oiled scientific and technological machine that is MIT, ACT is a strange creature, a hybrid where sometimes extremely different practices cross paths, producing exciting results: exhibitions; critical analyses, which often examine the foundations and the tendencies of the university itself, underpinned by an interest in the political role of research; actual inventions, developed in collaboration with other labs and university courses, that attract students who have a desire to exchange ideas with people from different paths and want the chance to take part in initiatives that operate free from educational preconceptions.
The book is one of the many avenues of communication pursued by ACT, currently directed by Gediminas Urbonas (a Lithuanian visual artist who has taught there since 2009) who succeeded the curator Ute Meta Bauer. The collection explores how the idea of public space is at the heart of what interests artists and designers and how, consequently, the conception, the creation and the use of collective spaces are a response to current-day transformations. These include the spread of digital technologies, climate change, the enforcement of austerity policies due to the reduction in available resources, and the emergence of political arguments that favour separation between people. The concluding conversation Reflexivity and Resistance in Communicative Capitalism between Urbonas and Jodi Dean, an American political scientist, summarises many of the book’s ideas: public space becomes the tool for resisting the growing privatisation of our lives.

The book, which features stupendous graphics by Node (a design studio based in Berlin and Oslo), is divided into four sections: paradoxes, ecologies, jurisdictions and signals.
The contents alternate essays (like Angela Vettese’s analysis of the role of national pavilions at the Biennale di Venezia or Beatriz Colomina’s reflections about the impact of social media on issues of privacy) with the presentation of architectural projects and artistic interventions designed by architects like Andrés Jaque, Teddy Cruz and Marjetica Potr or by historic MIT professors like the multimedia artist Antoni Muntadas. The republication of Art and Ecological Consciousness, a 1972 book by György Kepes, the multi-disciplinary genius who was the director of the Center for Advanced Visual Studies at MIT, proves that the institution has long been interested in these topics.


This collection of contributions supported by captivating iconography signals a basic optimism: the documented actions and projects and the consciousness that motivates the thinking of many creators proves there is a collective mobilisation, often starting from the bottom, that seeks out and creates the conditions for communal life. Even if it is never explicitly written, the answer to the question in the title is a resounding yes.



----------------------------------------------------
Public Space? Lost and Found
Gediminas Urbonas, Ann Lui and Lucas Freeman
SA + P Press, MIT School of Architecture and Planning
Cambridge MA, 2017
300 pages, $40
mit.edu
Overview
“Public space” is a potent and contentious topic among artists, architects, and cultural producers. Public Space? Lost and Found considers the role of aesthetic practices within the construction, identification, and critique of shared territories, and how artists or architects—the “antennae of the race”—can heighten our awareness of rapidly changing formulations of public space in the age of digital media, vast ecological crises, and civic uprisings.
Public Space? Lost and Found combines significant recent projects in art and architecture with writings by historians and theorists. Contributors investigate strategies for responding to underrepresented communities and areas of conflict through the work of Marjetica Potrč in Johannesburg and Teddy Cruz on the Mexico-U.S. border, among others. They explore our collective stakes in ecological catastrophe through artistic research such as atelier d’architecture autogérée’s hubs for community action and recycling in Colombes, France, and Brian Holmes’s theoretical investigation of new forms of aesthetic perception in the age of the Anthropocene. Inspired by artist and MIT professor Antoni Muntadas’ early coining of the term “media landscape,” contributors also look ahead, casting a critical eye on the fraught impact of digital media and the internet on public space.
This book is the first in a new series of volumes produced by the MIT School of Architecture and Planning’s Program in Art, Culture and Technology.
Contributors
atelier d'architecture autogérée, Dennis Adams, Bik Van Der Pol, Adrian Blackwell, Ina Blom, Christoph Brunner with Gerald Raunig, Néstor García Canclini, Colby Chamberlain, Beatriz Colomina, Teddy Cruz with Fonna Forman, Jodi Dean, Juan Herreros, Brian Holmes, Andrés Jaque, Caroline Jones, Coryn Kempster with Julia Jamrozik, György Kepes, Rikke Luther, Matthew Mazzotta, Metahaven, Timothy Morton, Antoni Muntadas, Otto Piene, Marjetica Potrč, Nader Tehrani, Troy Therrien, Gedminas and Nomeda Urbonas, Angela Vettese, Mariel Villeré, Mark Wigley, Krzysztof Wodiczko
With section openings from
Ana María León, T. J. Demos, Doris Sommer, and Catherine D'Ignazio
Friday, October 20. 2017
Note: More than a year ago, I posted about this move by Alphabet-Google toward becoming city designers... I tried to point out the problems related to a company which business is to collect data becoming the main investor in public space and common goods (the city is still part of the commons, isn't it?) But of course, this is, again, about big business ("to make the world a better place" ... indeed) and slick ideas.
But it is highly problematic that a company start investing in public space "for free". We all know what this mean now, don't we? It is not needed and not desired.
So where are the "starchitects" now? What do they say? Not much... Where are all the "regular" architects as well? Almost invisible, tricked in the wrong stakes, with -- I'm sorry...-- very few of them being only able to identify the problem.
This is not about building a great building for a big brand or taking a conceptual position, not even about "die Gestalt" anymore. It is about everyday life for 66% of Earth population by 2050 (UN study). It is, in this precise case, about information technologies and mainly information stategies and businesses that materialize into structures of life.
Shouldn't this be a major concern?
Via MIT Technology Review
-----
By Jamie Condliffe
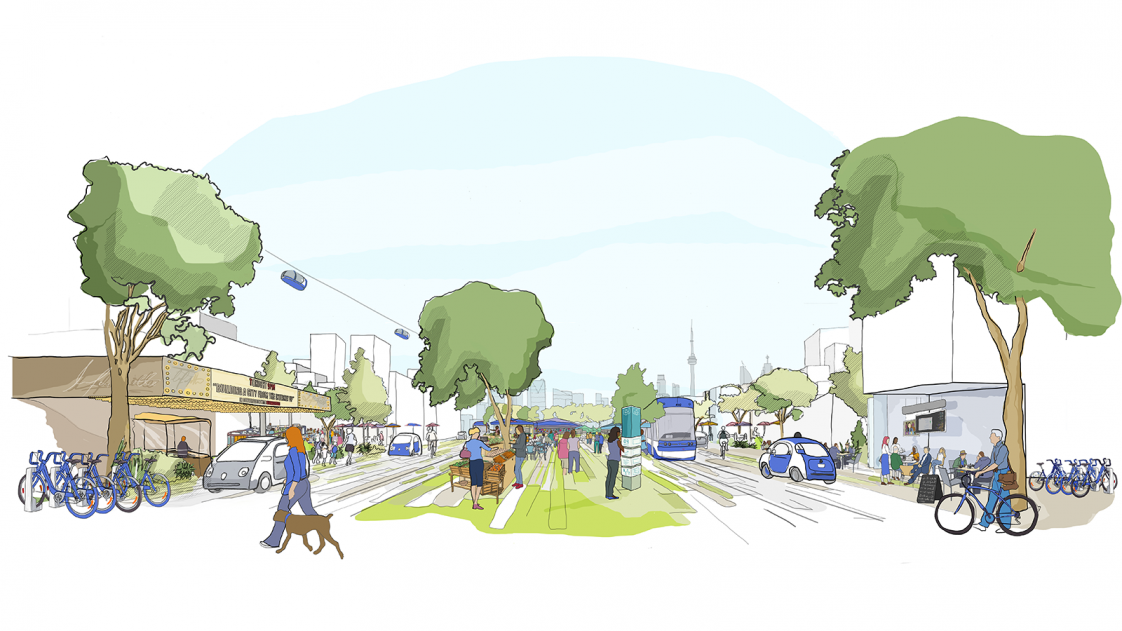

fabric | rblg legend: this hand drawn image contains all the marketing clichés (green, blue, clean air, bikes, local market, public transportation, autonomous car in a happy village atmosphere... Can't be further from what it will be).
An 800-acre strip of Toronto's waterfront may show us how cities of the future could be built. Alphabet’s urban innovation team, Sidewalk Labs, has announced a plan to inject urban design and new technologies into the city's quayside to boost "sustainability, affordability, mobility, and economic opportunity."
Huh?
Picture streets filled with robo-taxis, autonomous trash collection, modular buildings, and clean power generation. The only snag may be the humans: as we’ve said in the past, people can do dumb things with smart cities. Perhaps Toronto will be different.
Thursday, September 14. 2017
Note: we used references to China Mieville in past works (for example Heterochrony) to depict dual realities in some of our architectural devices. Yet in our case with a twist regarding the notion of narrative as it is described by Geoff Manaugh, even so the article mainly discuss the use of architecture and cities especially in a narrative (by Ch. Miéville), so as the relations between architecture and text here.
In the context of architecture and our personal work, I would rather tend to consider that an environment (built or natural) provides some kind of (open framing) for various narratives (in the same sense that a forest, for example, can host many narratives --from frightening to "feng shui"--, especially with changing conditions, yet by not being a specific narrative in itself, or maybe a very fuzzy narrative). It is not the purpose of a space to tell a story or even many stories therefore, but to be the host for stories, variable, multiple yet partly "framed" or contextualized.
I would rather consider that a space willing to tell a story is too "enclosed" and "enclosing" (a church for example). I prefer variations, some level of interactions en feedbacks and the capacity for the inhabitants of that space to take the environment (built or natural) as a base to create their own "stories", that will change and evolve over time.
Via BLDGBLOG
-----
By Geoff Manaugh (in 2011)

In his 2000 novel Perdido Street Station, for instance, an old industrial scrapyard on the underside of the city, full of discarded machine parts and used electronic equipment, suddenly bootstraps itself into artificial intelligence, self-rearranging into a tentacular and sentient system. In The Scar, a floating city travels the oceans, lashed together from the hulls of captured ships:
They were built up, topped with structure, styles and materials shoved together from a hundred histories and aesthetics into a compound architecture. Centuries-old pagodas tottered on the decks of ancient oarships, and cement monoliths rose like extra smokestacks on paddlers stolen from southern seas. The streets between the buildings were tight. They passed over the converted vessels on bridges, between mazes and plazas, and what might have been mansions. Parklands crawled across clippers, above armories in deeply hidden decks. Decktop houses were cracked and strained from the boats’ constant motion.
In his story “The Rope of the World,” originally published in Icon, a failed space elevator becomes the next Tintern Abbey, an awe-inspiring Romantic ruin in the sky. In “Reports Of Certain Events In London,” from the collection Looking for Jake, Miéville describes how constellations of temporary roads flash in and out through nighttime London, a shifting vascular geography of trap streets, only cataloged by the most fantastical maps.
And in his 2004 novel Iron Council, Miéville imagines something called “slow sculpture,” a geologically sublime new artform by which huge blocks of sandstone are “carefully prepared: shafts drilled precisely, caustic agents dripped in, for a slight and so-slow dissolution of rock in exact planes, so that over years of weathering, slabs would fall in layers, coming off with the rain, and at very last disclosing their long-planned shapes. Slow-sculptors never disclosed what they had prepared, and their art revealed itself only long after their deaths.”
BLDGBLOG has always been interested in learning how novelists see the city—how spatial descriptions of things like architecture and landscape can have compelling effects, augmenting both plot and emotion in ways that other devices, such as characterization, sometimes cannot. In earlier interviews with such writers as Patrick McGrath, Kim Stanley Robinson, Zachary Mason, Jeff VanderMeer, Tom McCarthy, and Mike Mignola, we have looked at everything from the literary appeal and narrative usefulness of specific buildings and building types to the descriptive influence of classical landscape painting, and we have entertained the idea that the demands of telling a good story often give novelists a more subtle and urgent sense of space even than architects and urban planners.
Over the course of the following long interview, China Miéville discusses the conceptual origins of the divided city featured in his recent, award-winning novel The City and The City; he points out the interpretive limitations of allegory, in a craft better served by metaphor; we take a look at the “squid cults” of Kraken (which arrives in paperback later this month) and maritime science fiction, more broadly; the seductive yet politically misleading appeal of psychogeography; J.G. Ballard and the clichés of suburban perversity; the invigorating necessities of urban travel; and much more.
...
BLDGBLOG: I’d like to start with The City and The City. What was your initial attraction to the idea of a divided city, and how did you devise the specific way in which the city would be split?
China Miéville: I first thought of the divided city as a development from an earlier idea I had for a fantasy story. That idea was more to do with different groups of people who live side-by-side but, because they are different species, relate to the physical environment very, very differently, having different kinds of homes and so on. It was essentially an exaggeration of the way humans and rats live in London, or something similar. But, quite quickly, that shifted, and I began to think about making it simply human.
For a long time, I couldn’t get the narrative. I had the setting reasonably clear in my head and, then, once I got that, a lot of things followed. For example, I knew that I didn’t want to make it narrowly, allegorically reductive, in any kind of lumpen way. I didn’t want to make one city heavy-handedly Eastern and one Western, or one capitalist and one communist, or any kind of nonsense like that. I wanted to make them both feel combined and uneven and real and full-blooded. I spent a long time working on the cities and trying to make them feel plausible and half-remembered, as if they were uneasily not quite familiar rather than radically strange.
I auditioned various narrative shapes for the book and, eventually, after a few months, partly as a present to my Mum, who was a big crime reader, and partly because I was reading a lot of crime at the time and thinking about crime, I started realizing what was very obvious and should have been clear to me much earlier. That’s the way that noir and hard-boiled and crime procedurals, in general, are a kind of mythic urbanology, in a way; they relate very directly to cities.
Once I’d thought of that, exaggerating the trope of the trans-jurisdictional police problem—the cops who end up having to be on each other’s beats—the rest of the novel just followed immediately. In fact, it was difficult to imagine that I hadn’t been able to work it out earlier. That was really the genesis.
I should say, also, that with the whole idea of a divided city there are analogies in the real world, as well as precursors within fantastic fiction. C. J. Cherryh wrote a book that had a divided city like that, in some ways, as did Jack Vance. Now I didn’t know this at the time, but I’m also not getting my knickers in a twist about it. If you think what you’re trying to do is come up with a really original idea—one that absolutely no one has ever had before—you’re just kidding yourself.
You’re inevitably going to tread the ground that the greats have trodden before, and that’s fine. It simply depends on what you’re able to do with it.

BLDGBLOG: Something that struck me very strongly about the book was that you manage to achieve the feel of a fantasy or science fiction story simply through the description of a very convoluted political scenario. The book doesn’t rely on monsters, non-humans, magical technologies, and so on; it’s basically a work of political science fiction.
Miéville: This is impossible to talk about without getting into spoiler territory—which is fine, I don’t mind that—but we should flag that right now for anyone who hasn’t read it and does want to read it.
But, yes, the overtly fantastical element just ebbed and ebbed, becoming more suggestive and uncertain. Although it’s written in such a way that there is still ambiguity—and some readers are very insistent on focusing on that ambiguity and insisting on it—at the same time, I think it’s a book, like all of my books, for which, on the question of the fantastic, you might want to take a kind of Occam’s razor approach. It’s a book that has an almost contrary relation to the fantastic, in a certain sense.
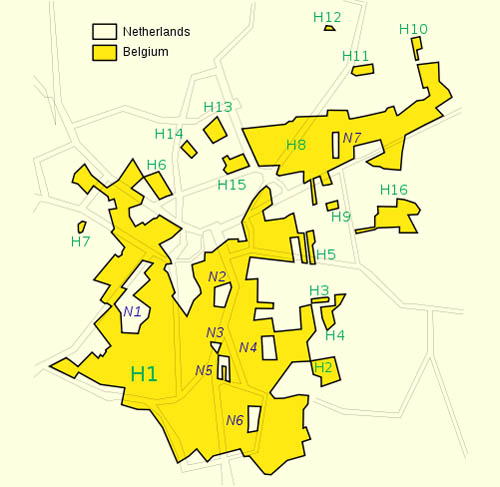
[Image: The marbled intra-national sovereignties of Baarle-Hertog].
BLDGBLOG: In some ways, it’s as if The City and The City simply describes an exaggerated real-life border condition, similar to how people live in Jerusalem or the West Bank, Cold War Berlin or contemporary Belfast—or even in a small town split by the U.S./Canada border, like Stanstead-Derby Line. In a sense, these settlements consist of next-door neighbors who otherwise have very complicated spatial and political relationships to one another. For instance, I think I sent you an email about a year ago about a town located both on and between the Dutch-Belgian border, called Baarle-Hertog.
Miéville: You did!
BLDGBLOG: I’m curious to what extent you were hoping to base your work on these sorts of real-life border conditions.
Miéville: The most extreme example of this was something I saw in an article in the Christian Science Monitor, where a couple of poli-sci guys from the State Department or something similar were proposing a solution to the Arab-Israeli conflict. In the case of Jerusalem, they were proposing basically exactly this kind of system, from The City and The City, in that you would have a single urban space in which different citizens are covered by completely different juridical relations and social relations, and in which you would have two overlapping authorities.
I was amazed when I saw this. I think, in a real world sense, it’s completely demented. I don’t think it would work at all, and I don’t think Israel has the slightest intention of trying it.
My intent with The City and The City was, as you say, to derive something hyperbolic and fictional through an exaggeration of the logic of borders, rather than to invent my own magical logic of how borders could be. It was an extrapolation of really quite everyday, quite quotidian, juridical and social aspects of nation-state borders: I combined that with a politicized social filtering, and extrapolated out and exaggerated further on a sociologically plausible basis, eventually taking it to a ridiculous extreme.
But I’m always slightly nervous when people make analogies to things like Palestine because I think there can be a danger of a kind of sympathetic magic: you see two things that are about divided cities and so you think that they must therefore be similar in some way. Whereas, in fact, in a lot of these situations, it seems to me that—and certainly in the question of Palestine—the problem is not one population being unseen, it’s one population being very, very aggressively seen by the armed wing of another population.
In fact, I put those words into Borlu’s mouth in the book, where he says, “This is nothing like Berlin, this is nothing like Jerusalem.” That’s partly just to disavow—because you don’t want to make the book too easy—but it’s also to make a serious point, which is that, obviously, the analogies will occur but sometimes they will obscure as much as they illuminate.
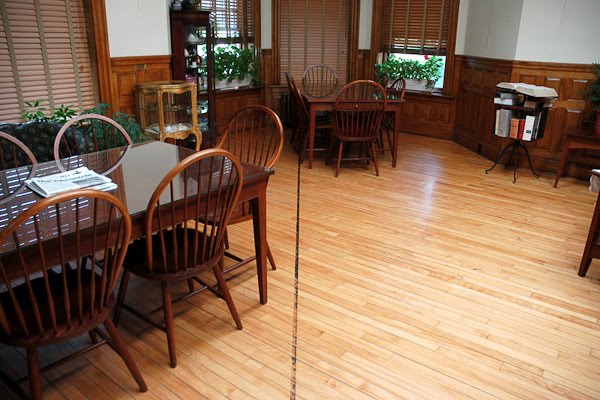

[Image: The international border between the U.S. and Canada passes through the center of a library; photo courtesy of the Center for Land Use Interpretation. “Technically, any time anyone crosses the international line, they are subject to having to report, in person, to a port of entry inspection station for the country they are entering,” CLUI explains. “Visiting someone on the other side of the line, even if the building is next door, means walking around to the inspection station first, or risk being an outlaw. Playing catch on Maple Street/Rue Ball would be an international event, and would break no laws presumably, so long as each time the ball was caught, the recipient marched over to customs to declare the ball.”].
BLDGBLOG: Your books often lend themselves to political readings, on the other hand. Do you write with specific social or political allegories in mind, and, further, how do your settings—as in The City and The City—come to reflect political intentions, spatially?
Miéville: My short answer is that I dislike thinking in terms of allegory—quite a lot. I’ve disagreed with Tolkien about many things over the years, but one of the things I agree with him about is this lovely quote where he talks about having a cordial dislike for allegory.
The reason for that is partly something that Frederic Jameson has written about, which is the notion of having a master code that you can apply to a text and which, in some way, solves that text. At least in my mind, allegory implies a specifically correct reading—a kind of one-to-one reduction of the text.
It amazes me the extent to which this is still a model by which these things are talked about, particularly when it comes to poetry. This is not an original formulation, I know, but one still hears people talking about “what does the text mean?”—and I don’t think text means like that. Texts do things.
I’m always much happier talking in terms of metaphor, because it seems that metaphor is intrinsically more unstable. A metaphor fractures and kicks off more metaphors, which kick off more metaphors, and so on. In any fiction or art at all, but particularly in fantastic or imaginative work, there will inevitably be ramifications, amplifications, resonances, ideas, and riffs that throw out these other ideas. These may well be deliberate; you may well be deliberately trying to think about issues of crime and punishment, for example, or borders, or memory, or whatever it might be. Sometimes they won’t be deliberate.
But the point is, those riffs don’t reduce. There can be perfectly legitimate political readings and perfectly legitimate metaphoric resonances, but that doesn’t end the thing. That doesn’t foreclose it. The text is not in control. Certainly the writer is not in control of what the text can do—but neither, really, is the text itself.
So I’m very unhappy about the idea of allegoric reading, on the whole. Certainly I never intend my own stuff to be allegorical. Allegories, to me, are interesting more to the extent that they fail—to the extent that they spill out of their own bounds. Reading someone like George MacDonald—his books are extraordinary—or Charles Williams. But they’re extraordinary to the extent that they fail or exceed their own intended bounds as Christian allegory.
When Iron Council came out, people would say to me: “Is this book about the Gulf War? Is this book about the Iraq War? You’re making a point about the Iraq War, aren’t you?” And I was always very surprised. I was like, listen: if I want to make a point about the Iraq War, I’ll just say what I think about the Iraq War. I know this because I’ve done it. I write political articles. I’ve written a political book. But insisting on that does not mean for a second that I’m saying—in some kind of unconvincing, “cor-blimey, I’m just a story-teller, guvnor,” type-thing—that these books don’t riff off reality and don’t have things to say about it.
There’s this very strange notion that a writer needs to smuggle these other ideas into the text, but I simply don’t understand why anyone would think that that’s what fiction is for.
BLDGBLOG: There are also very basic historical and referential limits to how someone might interpret a text allegorically. If Iron Council had been written twenty years from now, for instance, during some future war between Taiwan and China, many readers would think it was a fictional exploration of that, and they’d forget about the Iraq War entirely.
Miéville: Sure. And you don’t want to disavow these readings. You may think, at this point in this particular book, I actually do want to make a genuine policy prescription. With my hand on my heart, I don’t think I have ever done that, but, especially if you write with a political texture, you certainly have to take readings like this on the chin.
So, when people say: are you really talking about this? My answer is generally not no—it’s generally yes, but… Or yes, and… Or yes… but not in the way that you mean.

[Image: “The way a cop inhabits the city is doubtless a fascinating thing…” Photo courtesy of the NYPD].
BLDGBLOG: Let’s go back to the idea of the police procedural. It’s intriguing to compare how a police officer and a novelist might look at the city—the sorts of details they both might notice or the narratives they both might pick up on. Broadly speaking, each engages in detection—a kind of hermeneutics of urban space. How did this idea of urban investigation—the “mythic urbanology” you mentioned earlier—shape your writing of The City and The City?
Miéville: On the question of the police procedural and detection, for me, the big touchstones here were detective fiction, not real police. Obviously they are related, but they’re related in a very convoluted, mediated way.
What I wanted to do was write something that had a great deal of fidelity—hopefully not camp fidelity, but absolute rigorous fidelity—to certain generic protocols of policing and criminology. That was the drive, much more than trying to find out how police really do their investigations. The way a cop inhabits the city is doubtless a fascinating thing, but what was much more important to me for this book was the way that the genre of crime, as an aesthetic field, relates to the city.
The whole notion of decoding the city—the notion that, in a crime drama, the city is a text of clues, in a kind of constant, quantum oscillation between possibilities, with the moment of the solution really being a collapse and, in a sense, a kind of tragedy—was really important to me.
Of course, I’m not one of those writers who says I don’t read reviews. I do read reviews. I know that some readers were very dissatisfied with the strict crime drama aspect of it. I can only hold up my hands. It was extremely strict. I don’t mean to do that kind of waffley, unconvincing, writerly, carte blanche, get-out-clause of “that was the whole point.” Because you can have something very particular in mind and still fuck it up.
But, for me, given the nature of the setting, it was very important to play it absolutely straight, so that, having conceived of this interweaving of the cities, the actual narrative itself would remain interesting, and page-turning, and so on and so forth. I wanted it to be a genuine who-dunnit. I wanted it to be a book that a crime reader could read and not have a sense that I had cheated.
By the way, I love that formulation of crime-readers: the idea that a book can cheat is just extraordinary.
BLDGBLOG: Can you explain what you mean, in this context, by being rigorous? You were rigorous specifically to what?
Miéville: The book walks through three different kinds of crime drama. In section one and section two, it goes from the world-weary boss with a young, chippy sidekick to the mismatched partners who end up with grudging respect for each other. Then, in part three, it’s a political conspiracy thriller. I quite consciously tried to inhabit these different iterations of crime writing, as a way to explore the city.
But this has all just been a long-winded way of saying that I would not pretend or presume any kind of real policing knowledge of the way cities work. I suspect, probably, like most things, actual genuine policing is considerably less interesting than it is in its fictionalized version—but I honestly don’t know.



[Images: New York City crime scene photographs].
BLDGBLOG: There’s a book that came out a few years ago called The Meadowlands, by Robert Sullivan. At one point, Sullivan tags along with a retired detective in New Jersey who reveals that, now that he’s retired, he no longer really knows what to do with all the information he’s accumulated about the city over the years. Being retired means he basically knows thousands of things about the region that no longer have any real use for him. He thus comes across as a very melancholy figure, almost as if all of it was supposed to lead up to some sort of narrative epiphany—where he would finally and absolutely understand the city—but then retirement came along and everything went back to being slightly pointless. It was an interpretive comedown, you might say.
Miéville: That kind of specialized knowledge, in any field, can be intoxicating. If you experience a space—say, a museum—with a plumber, you may well come out with a different sense of the strengths and weaknesses of that museum—considering the pipework, as well, of course, as the exhibits—than otherwise. This is one reason I love browsing specialist magazines in fields about which I know nothing.
Obviously, then, with something that is explicitly concerned with uncovering and solving, it makes perfect sense that seeing the city through the eyes of a police detective would give you a very self-conscious view of what’s happening out there.
In terms of fiction, though, I think, if anything, the drive is probably the opposite. Novelists have an endless drive to aestheticize and to complicate. I know there’s a very strong tradition—a tradition in which I write, myself—about the decoding of the city. Thomas de Quincey, Michael Moorcock, Alan Moore, Neil Gaiman, Iain Sinclair—that type-thing. The idea that, if you draw the right lines across the city, you’ll find its Kabbalistic heart and so on.
The thing about that is that it’s intoxicating—but it’s also bullshit. It’s bullshit and it’s paranoia—and it’s paranoia in a kind of literal sense, in that it’s a totalizing project. As long as you’re constantly aware of that, at an aesthetic level, then it’s not necessarily a problem; you’re part of a process of urban mythologization, just like James Joyce was, I suppose. But the sense that this notion of uncovering—of taking a scalpel to the city and uncovering the dark truth—is actually real, or that it actually solves anything, and is anything other than an aesthetic sleight of hand, can be quite misleading, and possibly even worse than that. To the extent that those texts do solve anything, they only solve mysteries that they created in the first place, which they scrawled over the map of a mucky contingent mess of history called the city. They scrawled a big question mark over it and then they solved it.
Arthur Machen does this as well. All the great weird fiction city writers do it. Machen explicitly talks about the strength of London, as opposed to Paris, in that London is more chaotic. Although he doesn’t put it in these words, I think what partly draws him to London is this notion that, in the absence of a kind of unifying vision, like Haussmann’s Boulevards, and in a city that’s become much more syncretic and messy over time, you have more room to insert your own aestheticizing vision.
As I say, it’s not in and of itself a sin, but to think of this as a real thing—that it’s a lived political reality or a new historical understanding of the city—is, I think, a misprision.
BLDGBLOG: You can see this, as well, in the rise of psychogeography—or, at least, some popular version of it—as a tool of urban analysis in architecture today. This popularity often fails to recognize that, no matter how fun or poetic an experience it genuinely might be, randomly wandering around Boston with an iPhone, for instance, is not guaranteed to produce useful urban insights.
Miéville: Some really interesting stuff has been done with psychogeography—I’m not going to say it’s without uses other than for making pretty maps. I mean, re-experiencing lived urban reality in ways other than how one is more conventionally supposed to do so can shine a new light on things—but that’s an act of political assertion and will. If you like, it’s a kind of deliberate—and, in certain contexts, radical—misunderstanding. Great, you know—good on you! You’ve productively misunderstood the city. But I think that the bombast of these particular—what are we in now? fourth or fifth generation?—psychogeographers is problematic.
Presumably at some point we’re going to get to a stage, probably reasonably soon, in which someone—maybe even one of the earlier generation of big psychogeographers—will write the great book against psychogeography. Not even that it’s been co-opted—it’s just wheel-spinning.
BLDGBLOG: In an interview with Ballardian, Iain Sinclair once joked that psychogeography, as a term, has effectively lost all meaning. Now, literally any act of walking through the city—walking to work in the morning, walking around your neighborhood, walking out to get a bagel—is referred to as “psychogeography.” It’s as if the experience of being a pedestrian in the city has become so unfamiliar to so many people, that they now think the very act of walking around makes them a kind of psychogeographic avant-garde.
Miéville: It’s no coincidence, presumably, that Sinclair started wandering out of the city and off into fields.

[Image: Art by Vincent Chong for the Subterranean Press edition of Kraken].
BLDGBLOG: This brings us to something I want to talk about from Kraken, which comes out in paperback here in the States next week. In that book, you describe a group of people called the Londonmancers. They’re basically psychogeographers with a very particular, almost parodically mystical understanding of the city. How does Kraken utilize this idea of an occult geography of greater London?
Miéville: Yes, this relates directly to what we were just saying. For various reasons, some cities refract, through aesthetics and through art, with a particular kind of flamboyancy. For whatever reason, London is one of them. I don’t mean to detract from all the other cities in the world that have their own sort of Gnosticism, but it is definitely the case that London has worked particularly well for this. There are a couple of moments in the book of great sentimentality, as well, written, I think, when I was feeling very, very well disposed toward London.
I think, in those terms, that I would locate myself completely in the tradition of London phantasmagoria. I see myself as very much doing that kind of thing. But, at the same time, as the previous answer showed, I’m also rather ambivalent to it and sort of impatient with it—probably with the self-hating zeal of someone who recognizes their own predilections!
Kraken, for me, in a relatively light-hearted and comedic form, is my attempt to have it both ways: to both be very much in that tradition and also to take the piss out of it. Reputedly, throughout Kraken, the very act of psychogeographic enunciation and urban uncovering is both potentially an important plot point and something that does uncover a genuine mystery; but it is also something that is ridiculous and silly, an act of misunderstanding. It’s all to do with what Thomas Pynchon, in Gravity’s Rainbow, called kute korrespondences: “hoping to zero in on the tremendous and secret Function whose name, like the permuted names of God, cannot be spoken.”
The London within Kraken feels, to me, much more dreamlike than the London of something like King Rat. That’s obviously a much earlier book, and I now write very differently; but King Rat, for all its flaws, is a book very much to do with its time. It’s not just to do with London; it’s to do with London in the mid-nineties. It’s a real, particular London, phantasmagorized.
But Kraken is also set in London—and I wanted to indulge all my usual Londonisms and take them to an absurd extreme. The idea, for example, as you say, of this cadre of mages called the Londonmancers: that’s both in homage to parts of that tradition, and also, hopefully, an extension of it to a kind of absurdity—the ne plus ultra, you know?
BLDGBLOG: Kraken also makes some very explicit maritime gestures—the squid, of course, which is very redolent of H.P. Lovecraft, but also details such as the pirate-like duo of Goss and Subby. This maritime thread pops up, as well, in The Scar, with its floating city of linked ships. My question is: how do your interests in urban arcana and myth continue into the sphere of the maritime, and what narrative or symbolic possibilities do maritime themes offer your work?
Miéville: Actually, I think I was very restrained about Lovecraft. I think the book mentions Cthulhu twice—which, for a 140,000 or 150,000-word novel about giant squid cults, is pretty restrained! That’s partly because, as you say, if you write a book about a tentacular monster with a strange cult associated with it, anyone who knows the field is going to be thinking immediately in terms of Lovecraft. And I’m very, very impressed by Lovecraft—he’s a big presence for me—but, partly for that very reason, I think Kraken is one of the least Lovecrafty things I’ve done.
As to the question of maritimism, like a lot of my interests, it’s more to do with how it has been filtered through fiction, rather than how it is in reality. In reality, I have no interest in sailing. I’ve done it, I think, once.
But maritime fiction, from Gulliver’s Travels onward, I absolutely love. I love that it has its own set of traditions; in some ways, it’s a kind of mini-canon. It has its own riffs. There are some lovely teasings of maritime fiction within Gulliver’s Travels where he gets into the pornography of maritime terminology: mainstays and capstans and mizzens and so on, which, again, feature quite prominently in The Scar.

[Image: “An Imaginary View of the Arsenale” by J.M.W. Turner, courtesy of the Tate].
BLDGBLOG: In the context of the maritime, I was speaking to Reza Negarestani recently and he mentioned a Russian novella from the 1970s called “The Crew Of The Mekong,” suggesting that I ask you about your interest in it. Reza, of course, wrote Cyclonopedia, which falls somewhere between, say, H.P. Lovecraft and ExxonMobil, and for which you supplied an enthusiastic endorsement.
Miéville: Yes, I was blown away by Reza’s book—partly just because of the excitement of something that seems genuinely unclassifiable. It really is pretty much impossible to say whether you’re reading a work of genre fiction or a philosophical textbook or both of the above. There’s also the slightly crazed pseudo-rigor of it, and the sense that this is philosophy as inspired by schlocky horror movies as much as by Alain Badiou.
There’s a phrase that Kim Newman uses: post-genre horror. It’s a really nice phrase for something which is clearly inflected in a horror way, and clearly emerges out of the generic tradition of horror, but is no longer reducible to it. I think that Reza’s work is a very, very good example of that. As such, Cyclonopedia is one of my favorite books of the last few years.
BLDGBLOG: So Reza pointed me to “The Crew of the Mekong,” a work of Russian maritime scifi. The authors describe it, somewhat baroquely, as “an account of the latest fantastic discoveries, happenings of the eighteenth century, mysteries of matter, and adventures on land and at sea.” What drew you to it?
Miéville: I can’t remember exactly what brought me to it, to be perfectly honest: it was in a secondhand bookshop and I bought it because it looked like an oddity.
It’s very odd in terms of the shape of its narrative; it sort of lurches, with a story within a story, including a long, extended flashback within the larger framing narrative, and it’s all wrapped up in this pulp shell. In terms of the story itself, if I recall, it was actually me who suggested it to Reza because it has loads of stuff in it about oil, plastic resins, and pipelines, and one of the characters works for an institute called the Institute of Surfaces, which deals with the weird physics and uncanny properties of surfaces and topology.
Some of the flashback scenes and some of the background I’ve seen described as proto-steampunk, which I think is highly anachronistic: it’s more of an elective affinity, that, if you like retro-futurity, you might also like this. At a bare minimum, it’s a book worth reading simply because it’s very odd; at a maximum, some of the things going on it are philosophically interesting, although in a bizarre way.
But foreign pulp always has that peculiar kind of feeling to it, because you have a distinct cultural remove. At its worst, that can lead to an awful kind of orientalism, but it’s undeniably fascinating as a reader.
BLDGBLOG: It’s interesting that depictions of maritime journeys can maintain such strong mythic and imaginative resonance, even across wildly different cultures, eras, genres, and artforms—whether it’s “The Crew of the Mekong” or The Scar, Valhalla Rising or Moby Dick.
Miéville: The maritime world in general is an over-determined symbol of pretty much anything you want it to be—just fill in the blank: yearning, manifest destiny, whatever. It’s a very fecund field. My own interest in it comes pretty much through fiction and, to a certain extent, art. I wish I had a bit more money, in fact, because I would buy a lot of those fairly cheap, timeless, uncredited, late 19th-century, early 20th-century seascapes that you see on sale in a lot of thrift shops.
You also mentioned Goss and Subby. Goss and Subby themselves I never thought of as pirates, in fact. They were my go at iterating the much-masticated trope of the freakishly monstrous duo, figures who are, in some way that I suspect is politically meaningful, and that one day I’ll try to parse, generally even worse than their boss. They often speak in a somewhat odd, stilted fashion, like Hazel and Cha-Cha, or Croup and Vandemar, or various others. The magisterial TV Tropes has a whole entry on such duos called “Those Two Bad Guys.” The tweak that I tried to add with Goss and Subby was to integrate an idea from a Serbian fairy-tale called—spoiler!—“BasCelik.” For anyone who knows that story, this is a big give-away.
Again, though, I think you have to ration your own predilections. I have always been very faithful to my own loves: I look at my notebooks or bits of paper from when I was four and, basically, my interests haven’t changed. Left to my own devices, I would probably write about octopuses, monsters, occasionally Tarzan, and that’s really it. From a fairly young age, the maritime yarn was one of those.
But you can’t just give into your own drives, or you simply end up writing the same book again and again.
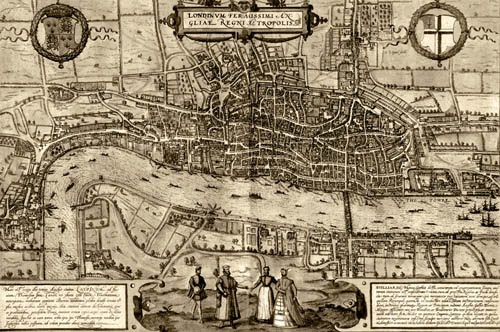
[Image: Mapping old London].
BLDGBLOG: Along those lines, are there any settings or environments—or even particular cities—that would be a real challenge for you to work with? Put another way, can you imagine giving yourself a deliberate challenge to write a novel set out in the English suburbs, or even in a place like Los Angeles? How might that sort of unfamiliar, seemingly very un-Miéville-like landscape affect your plots and characters?
Miéville: That’s a very interesting question. I really like that approach, in terms of setting yourself challenges that don’t come naturally. It’s almost a kind of Oulipo approach. It’s tricky, though, because you have to find something that doesn’t come naturally, but, obviously, you don’t want to write about something that doesn’t interest you. It has to be something that interests you contradictorally, or contrarily.
To be honest, the suburbs don’t attract me, for a bunch of reasons. I think it’s been done to death. I think anyone who tried to do that after J. G. Ballard would be setting themselves up for failure. As I tried to say when I did my review of the Ballard collection for The Nation, one of the problems is that, with an awful lot of suburban art today, it is pitched as this tremendously outré and radical claim to say that the suburbs are actually hotbeds of perversity—whereas, in fact, that is completely the cliché now. If you wanted to do something interesting, you would have to write about terribly boring suburbs, which would loop all the way back round again, out of interesting, through meta-interesting, and back down again to boring. So I doubt I would do something set in the suburbs.
I am quite interested in wilderness. Iron Council has quite a bit of wilderness, and that was something that I really liked writing and that I’d like to try again.
But, to be honest, it’s different kinds of urban space that appeal to me. If you’re someone who can’t drive, like I can’t, you find a lot of American cities are not just difficult, but really quite strange. I spend a lot of time in Providence, Rhode Island, and it’s a nice town, but it just doesn’t operate like a British town. A lot of American towns don’t. The number of American cities where downtown is essentially dead after seven o’clock, or in which you have these strange little downtowns, and then these quite extensive, sprawling but not quite suburban surroundings that all call themselves separate cities, that segue into each other and often have their own laws—that sort of thing is a very, very strange urban political aesthetic to me.
I’ve been thinking about trying to write a story not just set, for example, in Providence, but in which Providence, or another city that operates in a very non-English—or non-my-English—fashion, is very much part of the structuring power of the story. I’d be interested in trying something like that.
But countries all around the world have their own specificities about the way their urban environments work. I was in India recently, for example. It was a very brief trip, and I’m sure some of this was just wish fulfillment or aesthetic speculation, but I became really obsessed with the way, the moment you touched down at a different airport, you got out and you breathed the air, Mumbai felt different to Delhi, felt different to Kolkata, felt different to Chennai.
Rather than syncretizing a lot of those elements, I’d like to try to be really, really faithful to one or another city, which is not my city, in the hopes that, being an outsider, I might notice certain aspects that otherwise one would not. There’s a certain type of ingenuous everyday inhabiting of a city, which is very pre-theoretical for something like psychogeography, but it brings its own insights, particularly when it doesn’t come naturally or when it goes wrong.
There’s a lovely phrase that I think Algernon Blackwood used to describe someone’s bewilderment: he describes him as being bewildered in the way a man is when he’s looking for a post box in a foreign city. It’s a completely everyday, quotidian thing, and he might walk past it ten times, but he doesn’t—he can’t—recognize it.
That kind of very, very low-level alienation—the uncertainty about how do you hail a taxi, how do you buy food in this place, if somebody yells something from their top window, why does everyone move away from this part of the street and not that part? It’s that kind of very low-level stuff, as opposed to the kind of more obvious, dramatic differences, and I think there might be a way of tapping into that knowledge, knowledge that the locals don’t even think to tell you, that might be an interesting way in.
To that extent, it would be cities that I like but in which I’m very much an outsider that I’d like to try to tap.
• • •
Thanks to China Miéville for finding time to have this conversation, including scheduling a phone call at midnight in order to wrap up the final questions. Thanks, as well, to Nicola Twilley, who transcribed 95% of this interview and offered editorial feedback while it was in process, and to Tim Maly who first told me about the towns of Derby Line–Stanstead.
Miéville’s newest book, Embassytown, comes out in the U.S. in May; show your support for speculative fiction and pre-order a copy soon. If you are new to Miéville’s work, meanwhile, I might suggest starting with The City and The City.
Monday, November 23. 2015
Note: Meanwhile, on the "big architects" end of the spectrum... Where I enjoyed to read the sentence " Foster is delighted that Britain now has an infrastructure commission, chaired by Andrew Adonis, which he says gives the opportunity to plan in 30-year cycles and remove the politics from infrastructure."
Via The Guardian
-----
By Rowan Moore

Norman Foster’s Millau viaduct in France, which has ‘cut out five-hour traffic jams’. Photograph: Michael Reinhard/Corbis
“Do you believe in infrastructure?” asks Norman Foster, with challenge in his voice. He does. Infrastructure, he says, is about “investing not to solve the problems of today but to anticipate the issues of future generations”. He cites his hero, Joseph Bazalgette, who, in solving Victorian London’s sewage problems, “thought holistically to integrate drains with below-ground public transportation and above-ground civic virtue”.
Foster is delighted that Britain now has an infrastructure commission, chaired by Andrew Adonis, which he says gives the opportunity to plan in 30-year cycles and remove the politics from infrastructure. He will expound these views this week at the Urban Age 10th anniversary Global Debates, Urban Age being the LSE’s Deutsche Bank-sponsored series of conferences in which high-powered and highly powerful people travel the world exchanging views on city building.
Statistics spin out of him about sustainability. “If you take the carbon footprint of London, that’s one seventh of that of Atlanta, so there’s a relationship between density and emissions. The whole climate change issue, which many would argue is about the survival of the species, comes down to urbanism.

Foster’s proposed design for the Thames Hub airport. Photograph: dbox/Foster & Partners
“When I was in Harvard recently, I said that each of us in this room, the energy that we consume in one year would equal the energy consumed by two Japanese, 13 Chinese, 31 Indians and 370 Ethiopians. So you start to take the relationship between energy consumed by a society and infant mortality, life expectancy, sexual freedom, academic freedom, freedom from violence. So those societies that consume more energy have more of those desirable qualities, so all those issues are inseparable from the nature of the infrastructure.” The connections between these points are not always clear, but the argument seems to be that better use of energy through better infrastructure will enable more people to live better.
Of his own work, Foster says that many of the most important projects are not what are normally considered buildings, but things such as the Millennium Bridge, the pedestrianisation of Trafalgar Square in London, the Millau viaduct in southern France and the remaking of the Marseille waterfront. More statistics: “Millau cut out five-hour traffic jams, which meant that the saving in CO2 from the 10% of traffic that is heavy good vehicles had an effect equivalent to a forest of 40,000 trees.”
He has campaigned vigorously for the Thames Hub, a new airport in the Thames estuary with an associated network of huge ambition: an orbital railway around London, a flood barrier, tidal energy generation. He is profoundly disappointed that his plan is likely to be rejected in favour of an expanded Heathrow: “The reality of a hub airport is that you can never ever do that at Heathrow. If you do that at Heathrow now you can absolutely guarantee that we will still be pedalling furiously to stand still. You can never accommodate long-term needs there.”

Norman Foster: ‘The whole climate change issue comes down to urbanism.’ Photograph: Manolo Yllera
But given what he just said about sustainability, should we be expanding airports at all? “Do you eat meat?” he asks scathingly. “You’re probably going to have your hamburger in spite of the fact that you’re going to make a much greater impact than any travel.” Air travel, he says, “compares well statistically with the amount of methane produced by cows and the amount of energy and water needed to produce a hamburger”.
“The reality is that all society is embedded in mobility. You’re going to take that flight. You’d be better to take the flight out of an airport that is driven by tidal power and which uses natural light, and which anticipates the day when air travel will be more sustainable.” He talks of solar-powered flight and planes made of lightweight composite materials.
It could also be asked what is the role of the architect in what is generally the province of engineers, planners and politicians. Around us is evidence of his practice’s apparent potency – towers in China and India, a model of the giant circle, one mile in circumference, which will be Apple’s new headquarters, images of a concept for habitats on Mars – but Foster says: “I have no power as an architect, none whatsoever. I can’t even go on to a building site and tell people what to do.” Advocacy, he says, is the only power an architect ever has.
To write about Foster presents a particular challenge to an architecture critic. The scale of his achievement is immense and he has created many outstanding buildings. A wise man recently pointed out that if Foster had only built his 20 or 30 best works, critical admiration would be virtually unqualified. It is largely because his practice has designed many more projects than this that he sometimes gets a bad press. But would it really have been better if he had confined himself to a boutique practice in order to preserve his architectural purity?
It can seem peevish and petty to question his work, but it is not beyond criticism. In particular, it can become weaker the more it makes contact with realities outside itself. If you look upwards in the Great Court he designed in the British Museum, you will see an impressive structure of steel and glass, but at your own level it becomes bland and sometimes clumsy. The Gherkin is a memorable presence on the London skyline, but awkward at pavement level. The Millennium Bridge, even with the modifications necessary to stop it wobbling, is confident and elegant except at its landing, where the overhang of its cantilever creates spaces that are plain nasty.
In the context of infrastructure, the question is also whether it adapts to the political, social and physical conditions that surround it. In answer to Foster’s question, yes, I do believe in infrastructure. Or, rather, I’d compare it to water: essential to existence, life-enhancing and sometimes beautiful, but with the power to damage and destroy if misused.

Design for the proposed drone-port project in Rwanda. Photograph: Foster & Partners
All this makes a new drone-port project in Rwanda one of Foster and Partners’ most intriguing. Conceived with Jonathan Ledgard, the director of Afrotech, who describes himself as a thinker on the future of Africa, it is a plan to create a network of cargo drones that can bring medical supplies and blood, plus spare parts, electronics and e-commerce, to hard-to-access parts of Africa. The drones have ports – shelters where they can safely land and unload, but which also serve as “a health clinic, a digital fabrication shop, a post and courier room, and an e-commerce trading hub, allowing it to become part of local community life”. Because of their inaccessible locations, they have to be built using materials close to hand, so techniques have been developed for efficiently making local earth into bricks and stones into foundations.
It is impossible at this point and at this distance to know if the drone-port project will achieve what it hopes, but its ambition to adapt to local conditions seems absolutely to the point. The interesting question is then how to bring the same thinking to infrastructure in a developed country, such as Britain. What is the right infrastructure for the society and culture of this country, at this point? Has it changed since Foster’s Victorian heroes, such as Bazalgette, did their work? Can we import the large-scale thinking of modern China and, if so, with what modification? These are good questions for an architect to address.
Urban Age Global Debates run until 3 December; lsecities.net/ua
Thursday, April 09. 2015
Via Archdaily
-----
What if the manufacturers of the phones and social networks we cling to became the rulers of tomorrow’s cities? Imagine a world in which every building in your neighborhood is owned by Samsung, entire regions are occupied by the ghosts of our digital selves, and cities spring up in international waters to house outsourced laborers. These are the worlds imagined by self-described speculative architect, Liam Young in his latest series of animations entitled ”New City.” Read on after the break to see all three animations and learn more about what’s next in the series.
   

Viewers watching “The City in the Sea” at full size. Image Courtesy of Liam Young.
Liam Young’s London-based think tank Tomorrow’s Thoughts Today explores the “consequences of fantastic, speculative and imaginary urbanisms” through techniques of fiction and film, with extremely high definition animations accompanied by short stories written by Jeff Noon, Pat Cadigan and Tim Maughan. The imagery produced seeks to “help us explore the implications and consequences of emerging trends, technologies, and ecological conditions,” exploring emerging trends across media, technology, and popular culture in order to exaggerate them and better understand our own world alongside our future. The think-tank is being developed as a model for an architectural practice informed by research and speculation as products in and of themselves rather than buildings as final products. Animation is often employed by the think tank, as Liam Young tells ArchDaily:
“The skyline animations have been developed to be shown as super large scale projections, larger than the body so the audience has to move across the panorama, inhabiting it as they would do a city or building. Each animation is loaded with detail so as each time it is watched you might discover something different. The scale of the projections mean you are able to fully immerse yourself in the imaginary city and consumed by the soundscape you can sit and read the short story set in the city.”

From “Keeping up Appearances”. Image Courtesy of Liam Young
This latest series epitomizes many of the goals of the think-tank by looking at cites on a macro-scale and exaggerating trends across various stages of industry. The animations produced in the series thus far focus mainly on the technology sector and take existing cities as precedents for an exploration of themes and subsequent social commentary. For example, in the animation entitled “Keeping Up Appearances” (see top video) a future city is imagined in which almost every visible sign in the urban skyline is an advertisement for Samsung and the glowing logo represents the ownership of that particular piece of real estate. Based on a phenomenon occurring in many South Korean cities in which Samsung has begun to move into property development, in this exaggerated scenario the idea of corporate entities as driving forces behind real-estate development and growth becomes disturbingly plausible, while highlighting the real-world fact that many corporations have revenues which surpass the GDP of some countries. Young comments:
“The branded skyline is just the most visible consequence of our gadget allegiances. What I am suggesting is that our relationships to technology are in fact generating entirely new forms of city, and new notions of place or site itself. Where we are in the world matters far less now than how we are connected and who we are connected to. We now see new forms of city generated around operating system choices, who we like on facebook, our twitter network and so on. I am much closer to my virtual community than I am to my physical neighbors. The network has allowed ‘non state’ actors to permeate every aspect of our lives.”
The next video in the series, entitled “The City in the Sea,” looks at the very real issue of outsourced labor and industrialized cities in the developing world. Taken to its extreme in this animation, the imagined city is completely detached from any kind of nationalistic identity and only exists to provide a corporate haven for manufacturers that is devoid of regulations and taxes. According to Young:
“The City in the Sea is a multicultural city collaged from photos taken on expeditions through the outsourcing territories of India and China. The floating corporate city is built on the Pacific Ocean garbage patch and drifts in international waters, outside of national labor laws to become a free trade zone supporting the mega companies based on land. It is a city that connects to a long tradition of free states, from the traditions of pirate utopias, islands that existed with their own laws and governance to the speculations of offshore data havens on the abandoned naval fort Sealand or Google’s mysterious barges. We also see the same desires to escape jurisdiction playing out on land with the formation of special economic zones and free trade regions. These forms of territory are forcing us to reimagine what a border might mean in the age of the network.”
The third video in the series takes on a much more ephemeral quality and symbolically represents an element that is vital to our everyday lives, yet invisible to most. The idea of our online identity has become increasingly tangible to anyone that uses Facebook or surfs the web. Each of us possesses vast amounts of important information that is stored in “the cloud” but this notion has very little physical connection to our lives. Most are probably not aware of where their data is stored, but it is usually held in large data banks in places such as the city of Prineville, Oregon. These unassuming cities hold some of the world’s most sought after goods: personal identity stored digitally. Young also foresees data centers such as this as a new architectural frontier and describes its significance:
“This part of New City is built for machines, it is the physical landscape of the cloud, our generation’s cultural landscape. I am really interested in what these physical sites of the internet actually mean, they are a completely new cultural typology and architects need to take the data center on as a project. Is the internet a place to visit, are they sites of pilgrimage, spaces of congregation to be inhabited like a church on Sundays? Would we ever want to go and meet our digital selves, to gaze across server racks, and watch us winking back, in a million LEDs of Facebook blue? Every age has its iconic architectural typology. The dream commission was once the church, Modernism had the factory, then the house, in the recent decade we had the ‘starchitect’ museum and gallery. Now we have the data centre, the next forum for architectural culture.”

“The City in the Sea” on display at full size. Image Courtesy of Liam Young.
It is clear that the technology sector has already played a transformative role in our global economy, and Liam Young’s work gives us a glimpse at how technology may finally influence our built world. By illustrating these potential future scenarios and exaggerating them, Young opens a platform for discussion on how to take control of our own built world. But what is next in the series? What other pressing cultural issues require attention if we are to understand our built environment? Young tells ArchDaily:
“I am interested in continuing to look at the new types of ‘city’ that are emerging out of the network. Cities are increasingly being designed not for the people that occupy them but for the technologies and algorithms that are being built to understand them and manage them. Cities developed based around the logic of machine vision, satellite sight lines, Wi-Fi weather systems and so on are all of interest. These technologies are fundamentally changing what cities mean and these types of speculative projects are critical to play out possible scenarios for discussion.”

Viewers watching “Keeping Up Appearances” at full size. Image Courtesy of Liam Young
Readers can view all three animations accompanied with short stories by Jeff Noon, Pat Cadigan and Tim Maughan, at Liam Young’s Vimeo profile.
Wednesday, April 08. 2015
Via The Guardian
-----
By Steven Poole

Songdo in South Korea: a ‘smart city’ whose roads and water, waste and electricity systems are dense with electronic sensors. Photograph: Hotaik Sung/Alamy.
A woman drives to the outskirts of the city and steps directly on to a train; her electric car then drives itself off to park and recharge. A man has a heart attack in the street; the emergency services send a drone equipped with a defibrillator to arrive crucial minutes before an ambulance can. A family of flying maintenance robots lives atop an apartment block – able to autonomously repair cracks or leaks and clear leaves from the gutters.
Such utopian, urban visions help drive the “smart city” rhetoric that has, for the past decade or so, been promulgated most energetically by big technology, engineering and consulting companies. The movement is predicated on ubiquitous wireless broadband and the embedding of computerised sensors into the urban fabric, so that bike racks and lamp posts, CCTV and traffic lights, as well as geeky home appliances such as internet fridges and remote-controlled heating systems, become part of the so-called “internet of things” (the global market for which is now estimated at $1.7tn). Better living through biochemistry gives way to a dream of better living through data. You can even take an MSc in Smart Cities at University College, London.
Yet there are dystopian critiques, too, of what this smart city vision might mean for the ordinary citizen. The phrase itself has sparked a rhetorical battle between techno-utopianists and postmodern flâneurs: should the city be an optimised panopticon, or a melting pot of cultures and ideas?
And what role will the citizen play? That of unpaid data-clerk, voluntarily contributing information to an urban database that is monetised by private companies? Is the city-dweller best visualised as a smoothly moving pixel, travelling to work, shops and home again, on a colourful 3D graphic display? Or is the citizen rightfully an unpredictable source of obstreperous demands and assertions of rights? “Why do smart cities offer only improvement?” asks the architect Rem Koolhaas. “Where is the possibility of transgression?”

Smart beginnings: a crowd watches as new, automated traffic lights are erected at Ludgate Circus, London, in 1931. Photograph: Fox Photos/Getty Images
The smart city concept arguably dates back at least as far as the invention of automated traffic lights, which were first deployed in 1922 in Houston, Texas. Leo Hollis, author of Cities Are Good For You, says the one unarguably positive achievement of smart city-style thinking in modern times is the train indicator boards on the London Underground. But in the last decade, thanks to the rise of ubiquitous internet connectivity and the miniaturisation of electronics in such now-common devices as RFID tags, the concept seems to have crystallised into an image of the city as a vast, efficient robot – a vision that originated, according to Adam Greenfield at LSE Cities, with giant technology companies such as IBM, Cisco and Software AG, all of whom hoped to profit from big municipal contracts.
“The notion of the smart city in its full contemporary form appears to have originated within these businesses,” Greenfield notes in his 2013 book Against the Smart City, “rather than with any party, group or individual recognised for their contributions to the theory or practice of urban planning.”

Whole new cities, such as Songdo in South Korea, have already been constructed according to this template. Its buildings have automatic climate control and computerised access; its roads and water, waste and electricity systems are dense with electronic sensors to enable the city’s brain to track and respond to the movement of residents. But such places retain an eerie and half-finished feel to visitors – which perhaps shouldn’t be surprising. According to Antony M Townsend, in his 2013 book Smart Cities, Songdo was originally conceived as “a weapon for fighting trade wars”; the idea was “to entice multinationals to set up Asian operations at Songdo … with lower taxes and less regulation”.
In India, meanwhile, prime minister Narendra Modi has promised to build no fewer than 100 smart cities – a competitive response, in part, to China’s inclusion of smart cities as a central tenet of its grand urban plan. Yet for the near-term at least, the sites of true “smart city creativity” arguably remain the planet’s established metropolises such as London, New York, Barcelona and San Francisco. Indeed, many people think London is the smartest city of them all just now — Duncan Wilson of Intel calls it a “living lab” for tech experiments.
So what challenges face technologists hoping to weave cutting-edge networks and gadgets into centuries-old streets and deeply ingrained social habits and patterns of movement? This was the central theme of the recent “Re.Work Future Cities Summit” in London’s Docklands – for which two-day public tickets ran to an eye-watering £600.
The event was structured like a fast-cutting series of TED talks, with 15-minute investor-friendly presentations on everything from “emotional cartography” to biologically inspired buildings. Not one non-Apple-branded laptop could be spotted among the audience, and at least one attendee was seen confidently sporting the telltale fat cyan arm of Google Glass on his head.
“Instead of a smart phone, I want you all to have a smart drone in your pocket,” said one entertaining robotics researcher, before tossing up into the auditorium a camera-equipped drone that buzzed around like a fist-sized mosquito. Speakers enthused about the transport app Citymapper, and how the city of Zurich is both futuristic and remarkably civilised. People spoke about the “huge opportunity” represented by expanding city budgets for technological “solutions”.
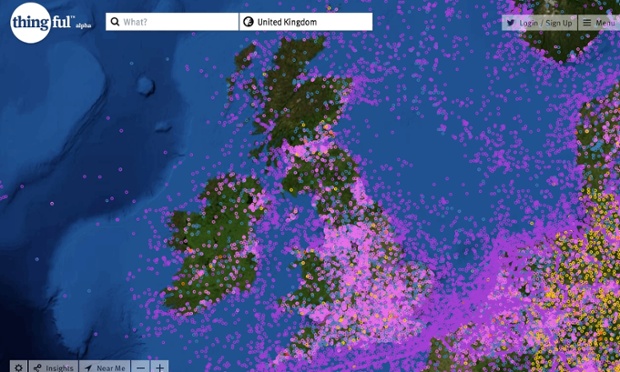
Usman Haque’s project Thingful is billed as a ‘search engine for the internet of things’
Strikingly, though, many of the speakers took care to denigrate the idea of the smart city itself, as though it was a once-fashionable buzzphrase that had outlived its usefulness. This was done most entertainingly by Usman Haque, of the urban consultancy Umbrellium. The corporate smart-city rhetoric, he pointed out, was all about efficiency, optimisation, predictability, convenience and security. “You’ll be able to get to work on time; there’ll be a seamless shopping experience, safety through cameras, et cetera. Well, all these things make a city bearable, but they don’t make a city valuable.”
As the tech companies bid for contracts, Haque observed, the real target of their advertising is clear: “The people it really speaks to are the city managers who can say, ‘It wasn’t me who made the decision, it was the data.’”
Of course, these speakers who rejected the corporate, top-down idea of the smart city were themselves demonstrating their own technological initiatives to make the city, well, smarter. Haque’s project Thingful, for example, is billed as a search engine for the internet of things. It could be used in the morning by a cycle commuter: glancing at a personalised dashboard of local data, she could check local pollution levels and traffic, and whether there are bikes in the nearby cycle-hire rack.
“The smart city was the wrong idea pitched in the wrong way to the wrong people,” suggested Dan Hill, of urban innovators the Future Cities Catapult. “It never answered the question: ‘How is it tangibly, materially going to affect the way people live, work, and play?’” (His own work includes Cities Unlocked, an innovative smartphone audio interface that can help visually impaired people navigate the streets.) Hill is involved with Manchester’s current smart city initiative, which includes apparently unglamorous things like overhauling the Oxford Road corridor – a bit of “horrible urban fabric”. This “smart stuff”, Hill tells me, “is no longer just IT – or rather IT is too important to be called IT any more. It’s so important you can’t really ghettoise it in an IT city. A smart city might be a low-carbon city, or a city that’s easy to move around, or a city with jobs and housing. Manchester has recognised that.”
One take-home message of the conference seemed to be that whatever the smart city might be, it will be acceptable as long as it emerges from the ground up: what Hill calls “the bottom-up or citizen-led approach”. But of course, the things that enable that approach – a vast network of sensors amounting to millions of electronic ears, eyes and noses – also potentially enable the future city to be a vast arena of perfect and permanent surveillance by whomever has access to the data feeds.
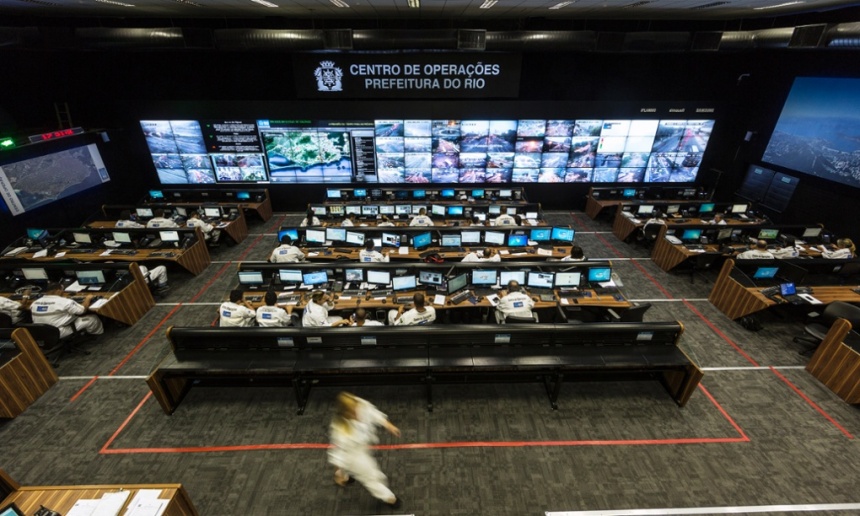

Inside Rio de Janeiro’s centre of operations: ‘a high-precision control panel for the entire city’. Photograph: David Levene
One only has to look at the hi-tech nerve centre that IBM built for Rio de Janeiro to see this Nineteen Eighty-Four-style vision already alarmingly realised. It is festooned with screens like a Nasa Mission Control for the city. As Townsend writes: “What began as a tool to predict rain and manage flood response morphed into a high-precision control panel for the entire city.” He quotes Rio’s mayor, Eduardo Paes, as boasting: “The operations centre allows us to have people looking into every corner of the city, 24 hours a day, seven days a week.”
What’s more, if an entire city has an “operating system”, what happens when it goes wrong? The one thing that is certain about software is that it crashes. The smart city, according to Hollis, is really just a “perpetual beta city”. We can be sure that accidents will happen – driverless cars will crash; bugs will take down whole transport subsystems or the electricity grid; drones could hit passenger aircraft. How smart will the architects of the smart city look then?
A less intrusive way to make a city smarter might be to give those who govern it a way to try out their decisions in virtual reality before inflicting them on live humans. This is the idea behind city-simulation company Simudyne, whose projects include detailed computerised models for planning earthquake response or hospital evacuation. It’s like the strategy game SimCity – for real cities. And indeed Simudyne now draws a lot of its talent from the world of videogames. “When we started, we were just mathematicians,” explains Justin Lyon, Simudyne’s CEO. “People would look at our simulations and joke that they were inscrutable. So five or six years ago we developed a new system which allows you to make visualisations – pretty pictures.” The simulation can now be run as an immersive first-person gameworld, or as a top-down SimCity-style view, where “you can literally drop policy on to the playing area”.
Another serious use of “pretty pictures” is exemplified by the work of ScanLAB Projects, which uses Lidar and ground-penetrating radar to make 3D visualisations of real places. They can be used for art installations and entertainment: for example, mapping underground ancient Rome for the BBC. But the way an area has been used over time, both above and below ground, can also be presented as a layered historical palimpsest, which can serve the purposes of archaeological justice and memory – as with ScanLAB’s Living Death Camps project with Forensic Architecture, on two concentration-camp sites in the former Yugoslavia.

The former German pavilion at Staro Sajmište, Belgrade – produced from terrestrial laser scanning and ground-penetrating radar as part of the Living Death Camps project. Photograph: ScanLAB Projects
For Simudyne’s simulations, meanwhile, the visualisations work to “gamify” the underlying algorithms and data, so that anyone can play with the initial conditions and watch the consequences unfold. Will there one day be convergence between this kind of thing and the elaborately realistic modelled cities that are built for commercial videogames? “There’s absolutely convergence,” Lyon says. A state-of-the art urban virtual reality such as the recreation of Chicago in this year’s game Watch Dogs requires a budget that runs to scores of millions of dollars. But, Lyon foresees, “Ten years from now, what we see in Watch Dogs today will be very inexpensive.”
What if you could travel through a visually convincing city simulation wearing the VR headset, Oculus Rift? When Lyon first tried one, he says, “Everything changed for me.” Which prompts the uncomfortable thought that when such simulations are indistinguishable from the real thing (apart from the zero possibility of being mugged), some people might prefer to spend their days in them. The smartest city of the future could exist only in our heads, as we spend all our time plugged into a virtual metropolitan reality that is so much better than anything physically built, and fail to notice as the world around us crumbles.
In the meantime, when you hear that cities are being modelled down to individual people – or what in the model are called “agents” – you might still feel a jolt of the uncanny, and insist that free-will makes your actions in the city unpredictable. To which Lyon replies: “They’re absolutely right as individuals, but collectively they’re wrong. While I can’t predict what you are going to do tomorrow, I can have, with some degree of confidence, a sense of what the crowd is going to do, what a group of people is going to do. Plus, if you’re pulling in data all the time, you use that to inform the data of the virtual humans.
“Let’s say there are 30 million people in London: you can have a simulation of all 30 million people that very closely mirrors but is not an exact replica of London. You have the 30 million agents, and then let’s have a business-as-usual normal commute, let’s have a snowstorm, let’s shut down a couple of train lines, or have a terrorist incident, an earthquake, and so on.” Lyons says you will get a highly accurate sense of how people, en masse, will respond to these scenarios. “While I’m not interested in a specific individual, I’m interested in the emergent behaviour of the crowd.”

City-simulation company Simudyne creates computerised models ‘with pretty pictures’ to aid disaster-response planning
But what about more nefarious bodies who are interested in specific individuals? As citizens stumble into a future where they will be walking around a city dense with sensors, cameras and drones tracking their every movement – even whether they are smiling (as has already been tested at the Cheltenham Jazz Festival) or feeling gloomy – there is a ticking time-bomb of arguments about surveillance and privacy that will dwarf any previous conversations about Facebook or even, perhaps, government intelligence agencies scanning our email. Unavoidable advertising spam everywhere you go, as in Minority Report, is just the most obvious potential annoyance. (There have already been “smart billboards” that recognised Minis driving past and said hello to them.) The smart city might be a place like Rio on steroids, where you can never disappear.
“If you have a mobile phone, and the right sensors are deployed across the city, people have demonstrated the ability to track those individual phones,” Lyon points out. “And there’s nothing that would prevent you from visualising that movement in a SimCity-like landscape, like in Watch Dogs where you see an avatar moving through the city and you can call up their social-media profile. If you’re trying to search a very large dataset about how someone’s moving, it’s very hard to get your head around it, but as soon as you fire up a game-style visualisation, it’s very easy to see, ‘Oh, that’s where they live, that’s where they work, that’s where their mistress must be, that’s where they go to drink a lot.’”
This is potentially an issue with open-data initiatives such as those currently under way in Bristol and Manchester, which is making publicly available the data it holds about city parking, procurement and planning, public toilets and the fire service. The democratic motivation of this strand of smart-city thinking seems unimpugnable: the creation of municipal datasets is funded by taxes on citizens, so citizens ought to have the right to use them. When presented in the right way – “curated”, if you will, by the city itself, with a sense of local character – such information can help to bring “place back into the digital world”, says Mike Rawlinson of consultancy City ID, which is working with Bristol on such plans.
But how safe is open data? It has already been demonstrated, for instance, that the openly accessible data of London’s cycle-hire scheme can be used to track individual cyclists. “There is the potential to see it all as Big Brother,” Rawlinson says. “If you’re releasing data and people are reusing it, under what purpose and authorship are they doing so?” There needs, Hill says, to be a “reframed social contract”.
The interface of Simudyne’s City Hospital EvacSim
Sometimes, at least, there are good reasons to track particular individuals. Simudyne’s hospital-evacuation model, for example, needs to be tied in to real data. “Those little people that you see [on screen], those are real people, that’s linking to the patient database,” Lyon explains – because, for example, “we need to be able to track this poor child that’s been burned.” But tracking everyone is a different matter: “There could well be a backlash of people wanting literally to go off-grid,” Rawlinson says. Disgruntled smart citizens, unite: you have nothing to lose but your phones.
In truth, competing visions of the smart city are proxies for competing visions of society, and in particular about who holds power in society. “In the end, the smart city will destroy democracy,” Hollis warns. “Like Google, they’ll have enough data not to have to ask you what you want.”
You sometimes see in the smart city’s prophets a kind of casual assumption that politics as we know it is over. One enthusiastic presenter at the Future Cities Summit went so far as to say, with a shrug: “Internet eats everything, and internet will eat government.” In another presentation, about a new kind of “autocatalytic paint” for street furniture that “eats” noxious pollutants such as nitrous oxide, an engineer in a video clip complained: “No one really owns pollution as a problem.” Except that national and local governments do already own pollution as a problem, and have the power to tax and regulate it. Replacing them with smart paint ain’t necessarily the smartest thing to do.
And while some tech-boosters celebrate the power of companies such as Über – the smartphone-based unlicensed-taxi service now banned in Spain and New Delhi, and being sued in several US states – to “disrupt” existing transport infrastructure, Hill asks reasonably: “That Californian ideology that underlies that user experience, should it really be copy-pasted all over the world? Let’s not throw away the idea of universal service that Transport for London adheres to.”
Perhaps the smartest of smart city projects needn’t depend exclusively – or even at all – on sensors and computers. At Future Cities, Julia Alexander of Siemens nominated as one of the “smartest” cities in the world the once-notorious Medellin in Colombia, site of innumerable gang murders a few decades ago. Its problem favelas were reintegrated into the city not with smartphones but with publicly funded sports facilities and a cable car connecting them to the city. “All of a sudden,” Alexander said, “you’ve got communities interacting” in a way they never had before. Last year, Medellin – now the oft-cited poster child for “social urbanism” – was named the most innovative city in the world by the Urban Land Institute.
One sceptical observer of many presentations at the Future Cities Summit, Jonathan Rez of the University of New South Wales, suggests that “a smarter way” to build cities “might be for architects and urban planners to have psychologists and ethnographers on the team.” That would certainly be one way to acquire a better understanding of what technologists call the “end user” – in this case, the citizen. After all, as one of the tribunes asks the crowd in Shakespeare’s Coriolanus: “What is the city but the people?”
Friday, January 23. 2015
Note: Following my recent posts about the research project "Inhabiting & Intercacing the Cloud(s)" I'm leading for ECAL, Nicolas Nova and I will be present during next Lift Conference in Geneva (Feb. 4-6 2015) for a talk combined with a workshop and a skype session with EPFL (a workshop related to the I&IC research project will be on the finish line at EPFL –Prof. Dieter Dietz’s ALICE Laboratory– on the day we’ll present in Geneva). If you plan to take part to Lift 15, please come say "hello" and exchange about the project.
Via the Lift Conference & iiclouds.org
—–
Inhabiting and Interfacing the Cloud(s)
Fri, Feb. 06 2015 – 10:30 to 12:30
Room 7+8 (Level 2)
Architect (EPFL), founding member of fabric | ch and Professor at ECAL
Principal at Near Future Laboratory and Professor at HEAD Geneva
Workshop description : Since the end of the 20th century, we have been seeing the rapid emergence of “Cloud Computing”, a new constructed entity that combines extensively information technologies, massive storage of individual or collective data, distributed computational power, distributed access interfaces, security and functionalism.
In a joint design research that connects the works of interaction designers from ECAL & HEAD with the spatial and territorial approaches of architects from EPFL, we’re interested in exploring the creation of alternatives to the current expression of “Cloud Computing”, particularly in its forms intended for private individuals and end users (“Personal Cloud”). It is to offer a critical appraisal of this “iconic” infrastructure of our modern age and its user interfaces, because to date their implementation has followed a logic chiefly of technical development, governed by the commercial interests of large corporations, and continues to be seen partly as a purely functional,centralized setup. However, the Personal Cloud holds a potential that is largely untapped in terms of design, novel uses and territorial strategies.
The workshop will be an opportunity to discuss these alternatives and work on potential scenarios for the near future. More specifically, we will address the following topics:
- How to combine the material part with the immaterial, mediatized part? Can we imagine the geographical fragmentation of these setups?
- Might new interfaces with access to ubiquitous data be envisioned that take nomadic lifestyles into account and let us offer alternatives to approaches based on a “universal” design? Might these interfaces also partake of some kind of repossession of the data by the end users?
- What setups and new combinations of functions need devising for a partly nomadic lifestyle? Can the Cloud/Data Center itself be mobile?
- Might symbioses also be developed at the energy and climate levels (e.g. using the need to cool the machines, which themselves produce heat, in order to develop living strategies there)? If so, with what users (humans, animals, plants)?
The joint design research Inhabiting & Interfacing the Cloud(s) is supported by HES-SO, ECAL & HEAD.
Interactivity : The workshop will start with a general introduction about the project, and moves to a discussion of its implications, opportunities and limits. Then a series of activities will enable break-out groups to sketch potential solutions.
Wednesday, October 15. 2014
Note: after the zoning for drones within cities, will we develop them with specific "city marks" dedicated for driverless cars? It reminds me a bit of this design research project done a few years ago, The New Robot Domesticity, which purpose was to design objects so that robots could also recognized/use them. Further away, it also remind me of a workshop we organized at the ECAL back in 2005 with researcher Frederic Kaplan (now head of Digital Humanities at EPFL) which purpose was to design artefacts for the Sony Aibo (a doc. video here). This later prtoject was realized in the frame of the research project Variable Environment.
Via MIT Technology Review
-----
Tricky intersections and rogue mechanical pedestrians will provide a testing area for automated and connected cars.
By Will Knight

The site of Ann Arbor’s driverless town, currently under construction.
A mocked-up set of busy streets in Ann Arbor, Michigan, will provide the sternest test yet for self-driving cars. Complex intersections, confusing lane markings, and busy construction crews will be used to gauge the aptitude of the latest automotive sensors and driving algorithms; mechanical pedestrians will even leap into the road from between parked cars so researchers can see if they trip up onboard safety systems.
The urban setting will be used to create situations that automated driving systems have struggled with, such as subtle driver-pedestrian interactions, unusual road surfaces, tunnels, and tree canopies, which can confuse sensors and obscure GPS signals.
“If you go out on the public streets you come up against rare events that are very challenging for sensors,” says Peter Sweatman, director of the University of Michigan’s Mobility Transformation Center, which is overseeing the project. “Having identified challenging scenarios, we need to re-create them in a highly repeatable way. We don’t want to be just driving around the public roads.”
Google and others have been driving automated cars around public roads for several years, albeit with a human ready to take the wheel if necessary. Most automated vehicles use accurate digital maps and satellite positioning, together with a suite of different sensors, to navigate safely.
Highway driving, which is less complex than city driving, has proved easy enough for self-driving cars, but busy downtown streets—where cars and pedestrians jockey for space and behave in confusing and surprising ways—are more problematic.
“I think it’s a great idea,” says John Leonard, a professor at MIT who led the development of a self-driving vehicle for a challenge run by DARPA in 2007. “It is important for us to try to collect statistically meaningful data about the performance of self-driving cars. Repeated operations—even in a small-scale environment—can yield valuable data sets for testing and evaluating new algorithms.”
The simulation is being built on the edge of the University of Michigan’s campus with funding from the Michigan Department of Transportation and 13 companies involved with developing automated driving technology. It is scheduled to open next spring. It will consist of four miles of roads with 13 different intersections.
Even Google, which has an ambitious vision of vehicle automation, acknowledges that urban driving is a significant challenge. Speaking at an event in California this July, Chris Urmson, who leads the company’s self-driving car project, said several common urban situations remain thorny (see “Urban Jungle a Tough Challenge for Google’s Autonomous Car”). Speaking with MIT Technology Review last month, Urmson gave further details about as-yet-unsolved scenarios (see “Hidden Obstacles for Google’s Self-Driving Cars”).
Such challenges notwithstanding, the first automated cars will go into production shortly. General Motors announced last month that a 2017 Cadillac will be the first car to offer entirely automated driving on highways. It’s not yet clear how the system will work—for example, how it will ensure that the driver isn’t too distracted to take the wheel in an emergency, or under what road conditions it might refuse to take the wheel—but in some situations, the car’s Super Cruise system will take care of steering, braking, and accelerating.
Another technology to be tested in the simulated town is vehicle-to-vehicle communications. The University of Michigan recently concluded a government-funded study in Ann Arbor involving thousands of vehicles equipped with transmitters that broadcast position, direction of travel, speed, and other information to other vehicles and to city infrastructure. The trial showed that vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure communications could prevent many common accidents by providing advanced warning of a possible collision.
“One of the interesting things, from our point of view, is what extra value you get by combining” automation and car-to-car communications, Sweatman says. “What happens when you put the two together—how much faster can you deploy it?”
Wednesday, October 01. 2014
Note: will the term "architect" be definitely overtaken by computer scientists? (rather the term "urbanist" in fact in this precise case, but still...). Will our environments be fully controlled by protocols, data sensing, bots and algorithms? Possibly... but who will design them? It makes me think that at one point, the music industry didn't think that their business would change so dramatically. We all know what happened but the good news is: we still need musicians!
So, I probably believe that architects and the schools that form them should look carefully to what is about to happen (the now already famous -- but still to come -- "Internet of Everything"). New actors (in the building industry) are pushing hard for their place in this "still to come" field that include the construction, monitoring and control of cities, territories, buildings, houses, ... (IBM, Cisco, Google, Apple, etc.). Their hidden lines of code will become much more significant for the life of urban citizens (because of their increasing impact on "the way life goes") than any "new" 3d shape you can possibly imagine. Shape is over, code is coming in a street near you!
Via The Verge
-----
The world's got problems and the Google CEO is searching for solutions
By Vlad Savov

As if self-driving cars, balloon-carried internet, or the eradication of death weren't ambitious enough projects, Google CEO Larry Page has apparently been working behind the scenes to set up even bolder tasks for his company. The Information reports that Page started up a Google 2.0 project inside the company a year ago to look at the big challenges facing humanity and the ways Google can overcome them. Among the grand-scale plans discussed were Page's desire to build a more efficient airport as well as a model city. To progress these ideas to fruition, the Google chief has also apparently proposed a second research and development lab, called Google Y, to focus on even longer-term programs that the current Google X, which looks to support future technology and is headed up by his close ally Sergey Brin.
More about it HERE.
|










































