Sticky Postings
All 242 fabric | rblg updated tags | #fabric|ch #wandering #reading
By fabric | ch
-----
As we continue to lack a decent search engine on this blog and as we don't use a "tag cloud" ... This post could help navigate through the updated content on | rblg (as of 09.2023), via all its tags!
FIND BELOW ALL THE TAGS THAT CAN BE USED TO NAVIGATE IN THE CONTENTS OF | RBLG BLOG:
(to be seen just below if you're navigating on the blog's html pages or here for rss readers)
--
Note that we had to hit the "pause" button on our reblogging activities a while ago (mainly because we ran out of time, but also because we received complaints from a major image stock company about some images that were displayed on | rblg, an activity that we felt was still "fair use" - we've never made any money or advertised on this site).
Nevertheless, we continue to publish from time to time information on the activities of fabric | ch, or content directly related to its work (documentation).
Tuesday, February 27. 2024
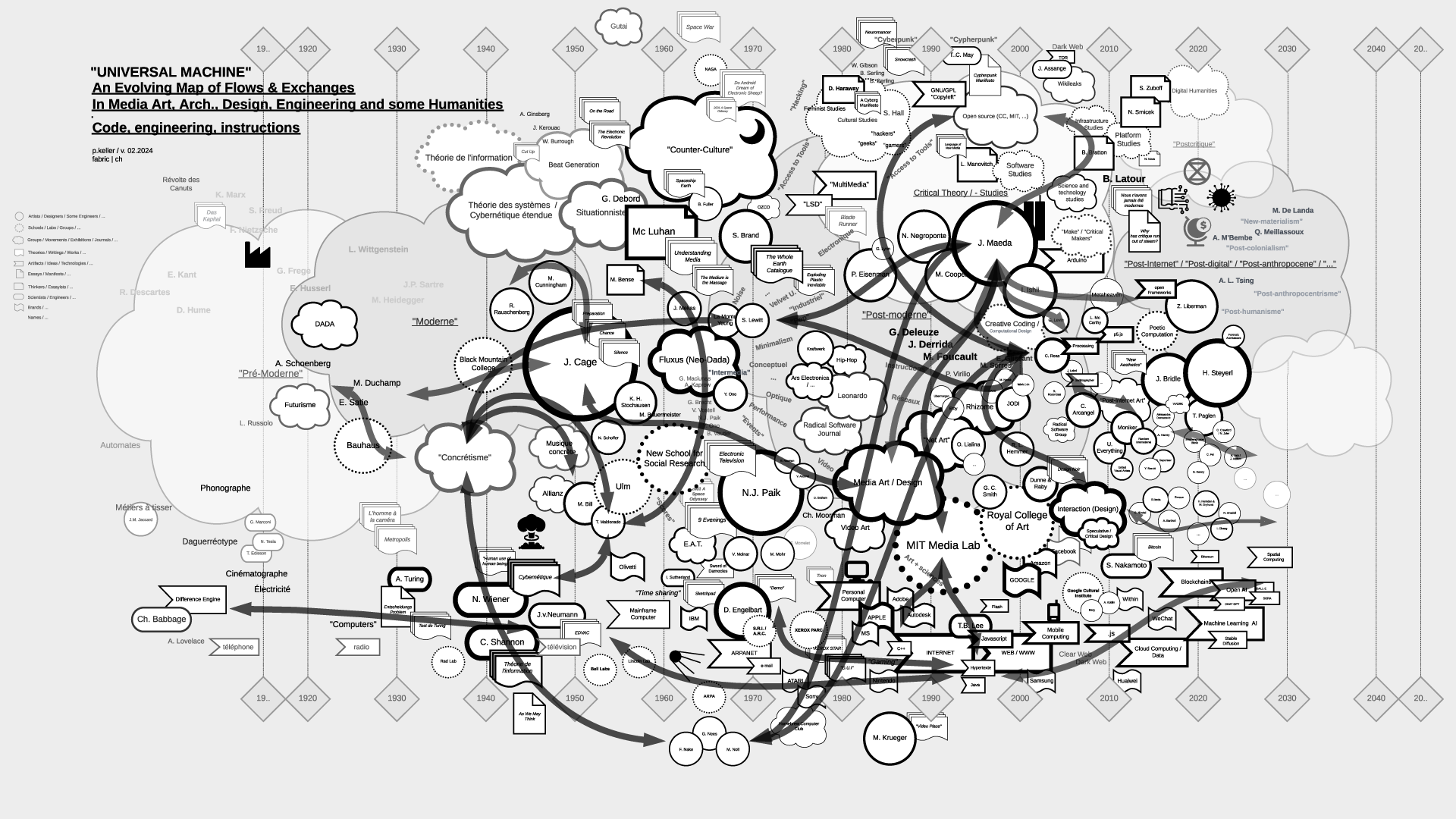
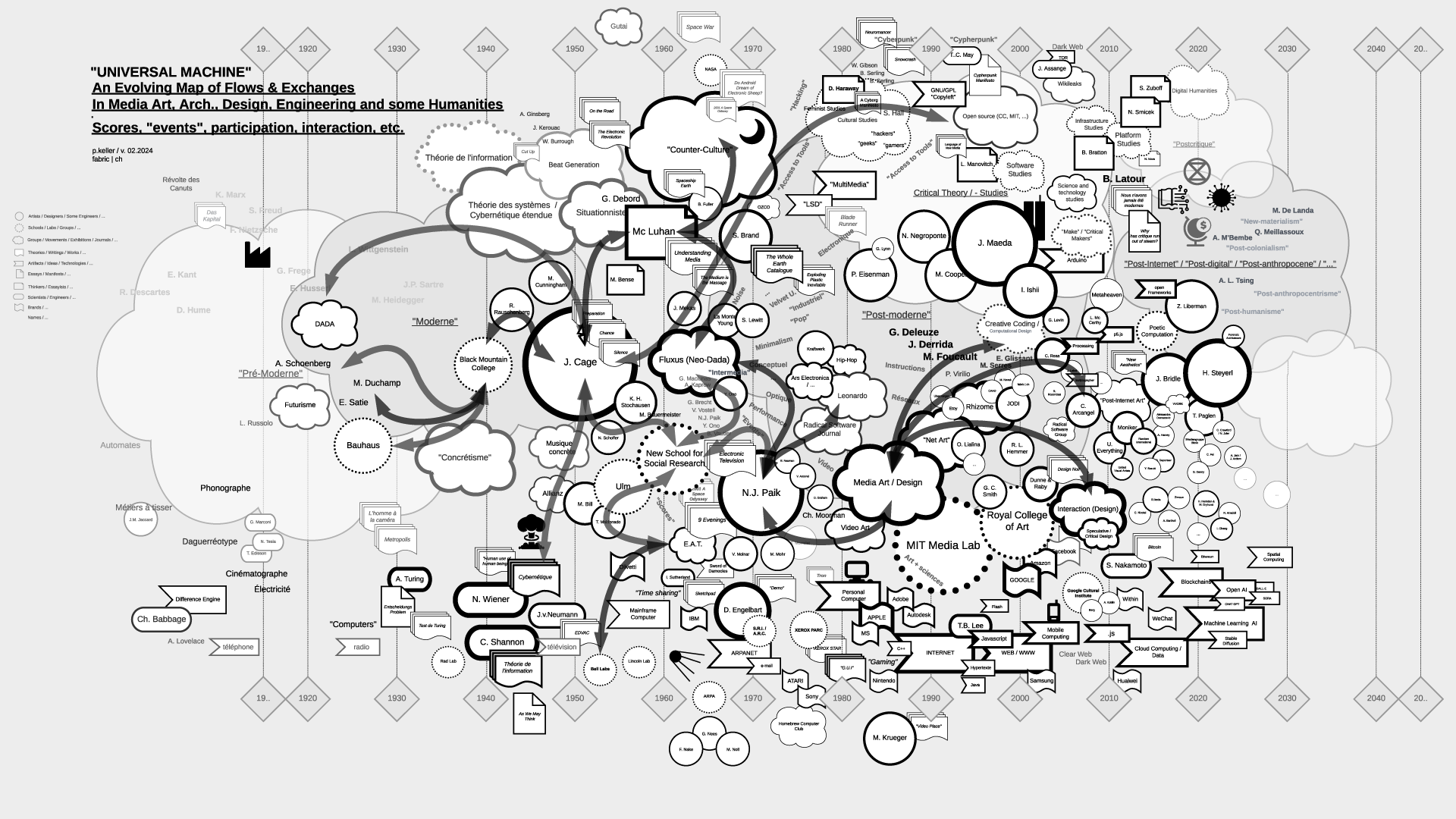
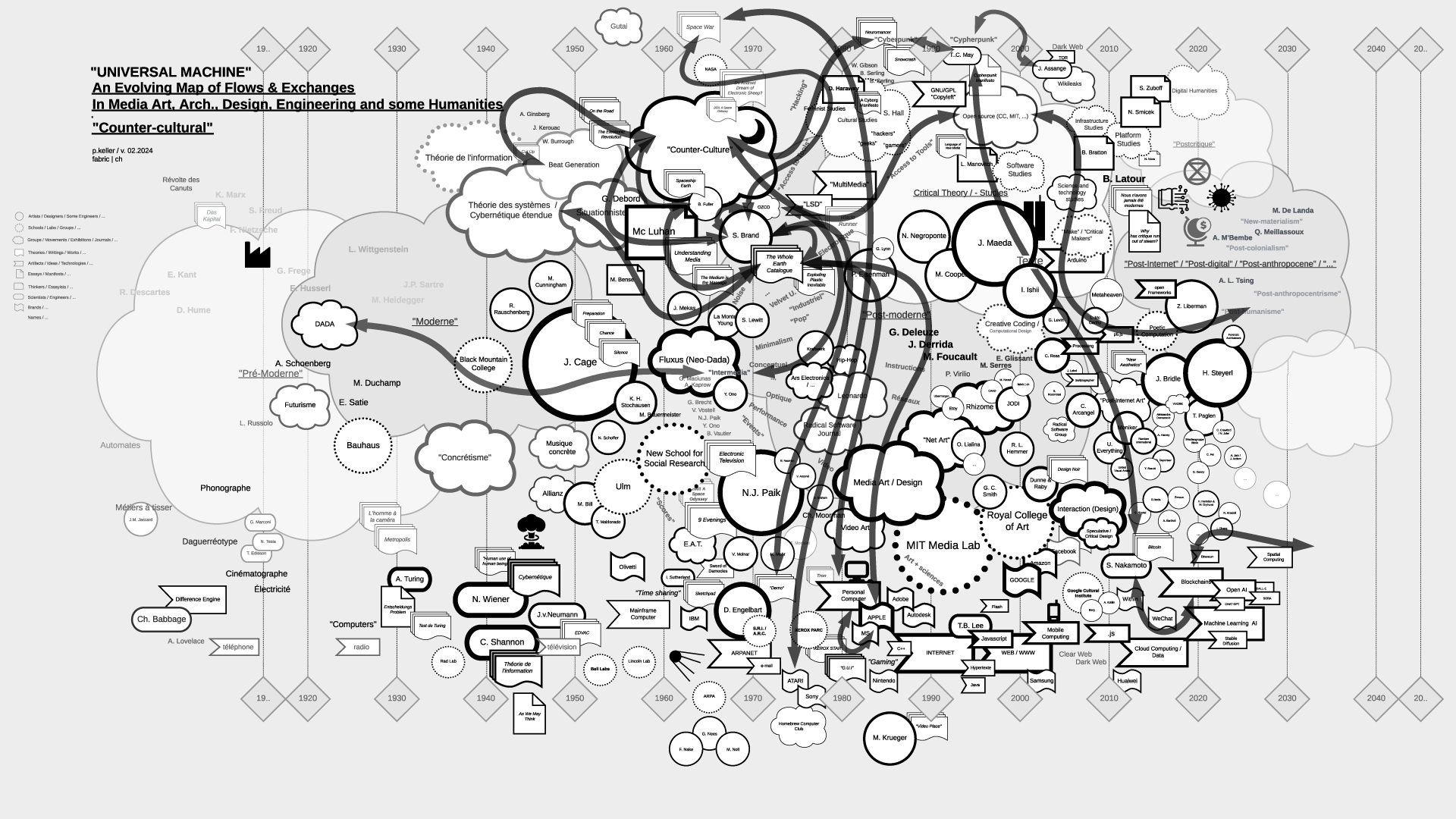
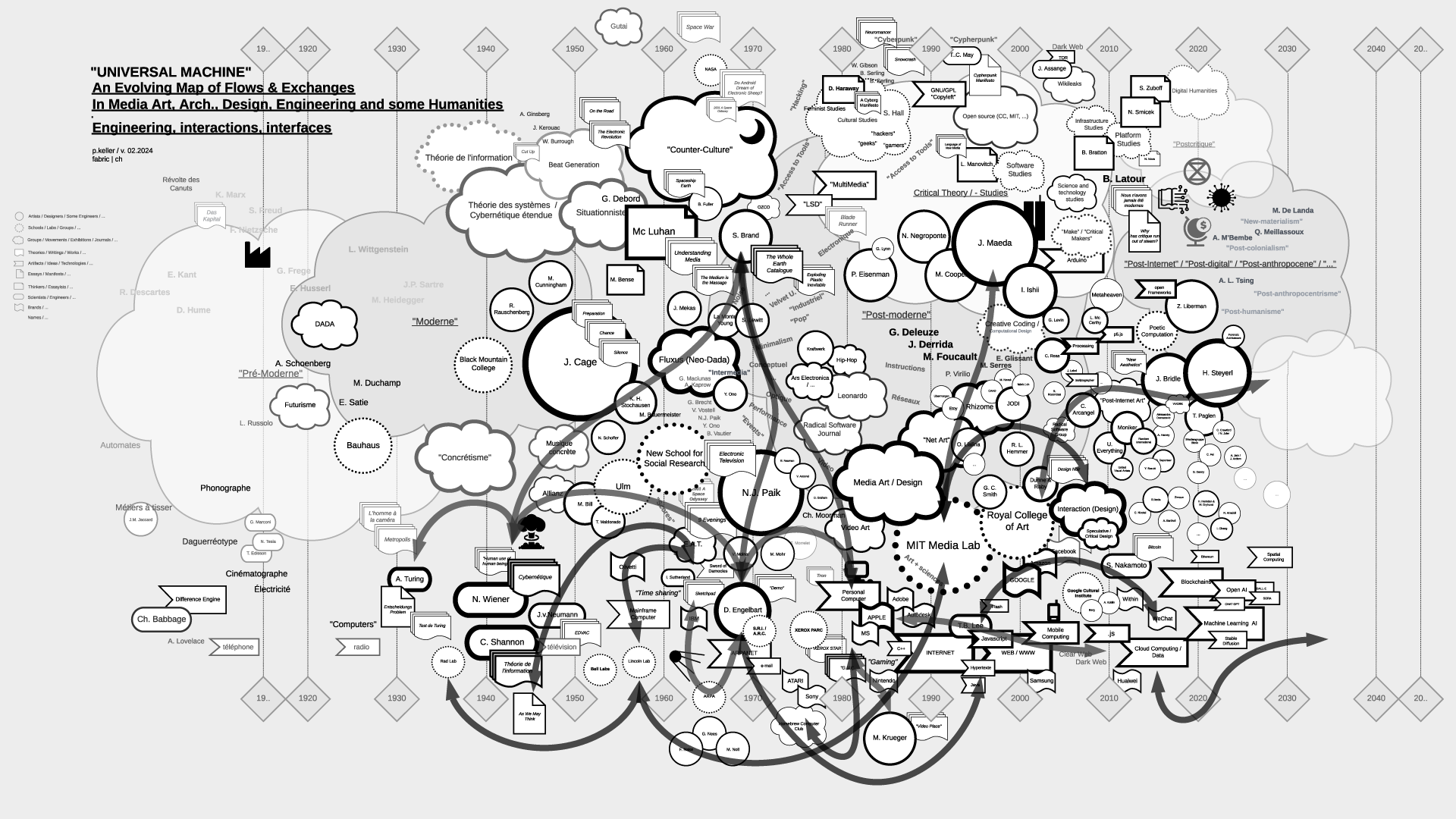
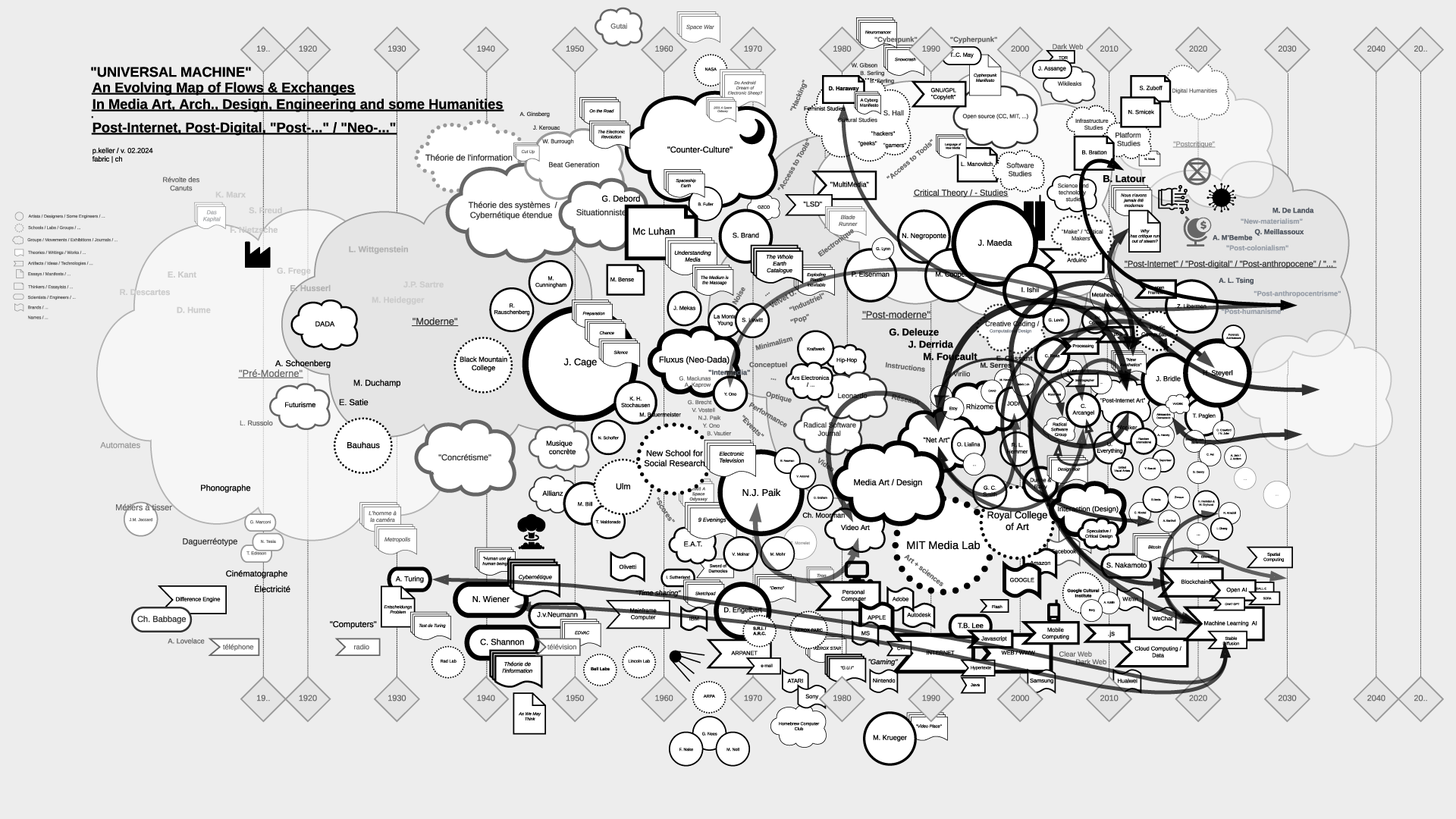
"Universal Machine": historical graphs on the relations and fluxes between art, architecture, design, and technology (19.. - 20..) | #art&sciences #history #graphs
Note (03.2024): The contents of the files (maps) have been updated as of 02.2024.
-
Note (07.2021): As part of my teaching at ECAL / University of Art and Design Lausanne (HES-SO), I've delved into the historical ties between art and science. This ongoing exploration focuses on the connection between creative processes in art, architecture, and design, and the information sciences, particularly the computer, also known as the "Universal Machine" as coined by A. Turing. This informs the title of the graphs below and this post.
Through my work at fabric | ch, and previously as an assistant at EPFL followed by a professorship at ECAL, to experience first hand some of these massive transformations in society and culture.
Thus, in my theory courses, I've aimed to create "maps" that aid in comprehending, visualizing, and elucidating the flux and timelines of interactions among individuals, artifacts, and disciplines. These maps, imperfect and constrained by size, are continuously evolving and open to interpretation beyond my own. I regularly update them as part of the process.
Yet, in the absence of a comprehensive written, visual, or sensitive history of these techno-cultural phenomena as a whole, these maps serve as valuable approximation tools for grasping the flows and exchanges that either unite or divide them. They offer a starting point for constructing personal knowledge and delving deeper into these subjects.
This is precisely why, despite their inherent fuzziness - or perhaps because of it - I choose to share them on this blog (fabric | rblg), in an informal manner. It's an invitation for other artists, designers, researchers, teachers, students, and so forth, to begin building upon them, to depict different flows, to develop pre-existing or subsequent ideas, or even more intriguingly, to diverge from them. If such advancements occur, I'm keen on featuring them on this platform. Feel free to reach out for suggestions, comments, or to share new developments.
...
It's worth mentioning that the maps are structured horizontally along a linear timeline, spanning from the late 18th century to the mid-21st century, predominantly focusing on the industrial period. Vertically, they are organized around disciplines, with the bottom representing engineering, the middle encompassing art and design, and the top relating to humanities, social events, or movements.
Certainly, one might question this linear timeline, echoing the sentiments of writer B. Latour. What about considering a spiral timeline, for instance? Such a representation would still depict both the past and the future, while also illustrating the historical proximities of topics, connecting past centuries and subjects with our contemporary context in a circular manner. However, for the time being, and while recognizing its limitations, I adhere to the simplicity of the linear approach.
Countless narratives can emerge as inherent properties of the graphs, underscoring that they are not their origins but rather products thereof.
...
The selection of topics (code, scores-instructions, countercultural, network-related, interaction, "post-...") currently aligns with the themes of my teaching but is subject to expansion, possibly toward an underlying layer revealing the material conditions that underpinned and facilitated the entire process.
In any case, this could serve as a fruitful starting point for some further readings or perhaps a new "Where's Waldo/Wally" kind of game!
Via fabric | ch
-----
By Patrick Keller
Rem.: By clicking on the thumbnails below you'll get access to HD versions.
"Universal Machine", main map (late 18th to mid 21st centuries):
Flows in the map > "Code":
Flows in the map > "Scores, Partitions, ...":
Flows in the map > "Countercultural, Subcultural, ...":
Flows in the map > "Network Related":
Flows in the map > "Interaction":
Flows in the map > "Post-Internet/Digital, "Post -..." , "Neo -...", ML/AI":
...
To be continued (& completed) ...
Tuesday, July 18. 2023
fabric | ch at Centre Pompidou for Moviment (Ch. 9, "Par-delà la matière") | #hybrid #exhibition #centrepompidou #matter #non-matter #LesImmatériaux
Note: fabric | ch presented its recent works at the Centre Pompidou in early July, as part of the Moviment program of exhibitions/performances/conferences/projections. We took part in Chapter 9: Beyond Matter.
The focus of the weekend was a return to the historic exhibition "Les Immatériaux" (1985, cur. T. Chaput & J.F. Lyotard) and the contemporary questioning of the postmodern period.
Participants included artists who took part in Les Immatériaux (J.-L. Boissier, K. Thomadaki, J.-C. Fall), as well as contemporary curators such as H.-U. Obrist and D. Birnbaum, so as artists and filmmakers P. Parreno, A. Serra and philosopher A. Longo.
Via @ptrckkllr
-----
Thursday, June 29. 2023
Atomized (re-)Staging by fabric | ch at Centre Pompidou | #exhibitions #digital #revival #iconoclash #immatériaux
Note: At the invitation of Macella Lista and Livia Nolasco-Roszas (curators), fabric | ch presents Atomized (re-)Staging during the Moviment festival-exhibition at the Centre Pompidou in Paris, as part of a weekend devoted to a return to the landmark exhibition Les Immatériaux (which took place at Beaubourg in 1985).
Via @ptrckkllr and @beyondmatereu (research project & exhibition: Beyond Matter)
-----
Monday, March 13. 2023
Atomized (re-)Staging short video documentation | #fabricch #digital #hybrid #exhibition
Note: a brief video documentation about one of fabric | ch's latest project – Atomized (Re)Staging – that was exhibited at ZKM during Matter. Non-Matter. Anti-Matter.
The exhibition was curated by Lívía Nolasco-Roszás and Felix Koberstein and took place ibn the context of the European research project Beyond Matter.
![]()
-----
Wednesday, November 30. 2022
Past exhibitions as Digital Experiences @ZKM, fabric | ch | #digital #exhibition #experimentation
Note:
The exhibition related to the project and European research Beyond Matter - Past Exhibitions as Digital Experiences will open next week at ZKM, with the digital versions (or should I rather say "versioning"?) of two past and renowned exhibitions: Iconoclash, at ZKM in 2002 (with Bruno Latour among the multiple curators) and Les Immateriaux, at Beaubourg in 1985 (in this case with Jean-François Lyotard, not so long after the release of his Postmodern Condition). An unusual combination from two different times and perspectives.
The title of the exhibition will be Matter. Non-Matter. Anti-Matter, with an amazing contemporary and historic lineup of works and artists, as well as documentation material from both past shows.
Working with digitized variants of iconic artworks from these past exhibitions (digitization work under the supervision of Matthias Heckel), fabric | ch has been invited by Livia Nolasco-Roszas, ZKM curator and head of the research, to present its own digital take in the form of a combination on these two historic shows, and by using the digital models produced by their research team and made available.

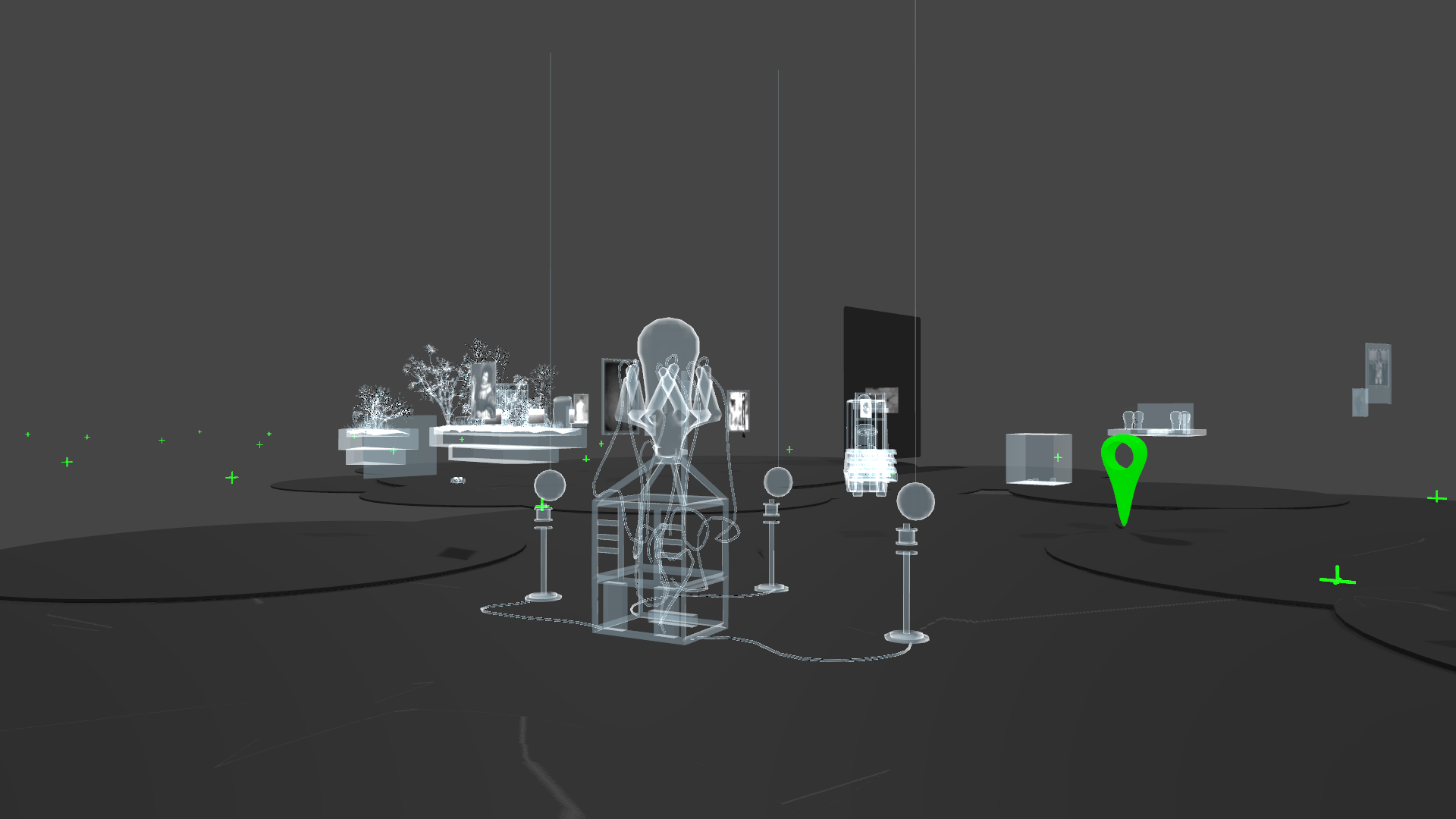

The result, a new fabric | ch project entitled Atomized (re-)Staging, will be presented at the ZKM in Karlsruhe from this Saturday on (03.12.2022 - 23.04.2023).
Via ZKM
-----

Opening: Matter. Non-Matter. Anti-Matter.
© ZKM | Center for Art and Media Karlsruhe, Visual: AKU Collective / Mirjam Reili
Past exhibitions as Digital Experiences
Fri, December 02, 2022 7 pm CET, Opening
---
Free entry
---
When past exhibitions come to life digitally, the past becomes a virtual experience. What this novel experience can look like in concrete terms is shown by the exhibition »Matter. Non-Matter. Anti-Matter«.
As part of the project »Beyond Matter. Cultural Heritage on the Verge of Virtual Reality«, the ZKM | Karlsruhe and the Centre Pompidou, Paris, use the case studies »Les Immatériaux« (Centre Pompidou, 1985) and »Iconoclash« (ZKM | Karlsruhe, 2002) to investigate the possibility of reviving exhibitions through experiential methods of digital and spatial modeling.
The digital model as an interactive presentation of exhibition concepts is a novel approach to exploring exhibition history, curatorial methods, and representation and mediation. The goal is not to create »digital twins«, that is, virtual copies of past assemblages of artifacts and their surrounding architecture, but to provide an independent sensory experience.
On view will be digital models of past exhibitions, artworks and artifacts from those exhibitions, and accompanying contemporary commentary integrated via augmented reality. The exhibition will be accompanied by a conference on virtualizing exhibition histories.
The exhibition will be accompanied by numerous events, such as specialist workshops, webinars, online and offline guided tours, and a conference.
---
Program
7 – 7:30 p.m. Media Theater
Short lectures by
Sybille Krämer, Professor (emer.) at the Free University of Berlin
Siegfried Zielinski, media theorist with a focus on archaeology and variantology of arts and media, curator, author
Moderation: Lívia Nolasco-Rózsás, curator
7:30 – 8:15 p.m. Media Theater
Welcome
Olga Sismanidi, Representative Creative Europe Program of the European Commission (EACEA)
Arne Braun, State Secretary in the Ministry of Science, Research and the Arts of Baden-Württemberg
Frank Mentrup, Lord Mayor of the City of Karlsruhe
Peter Weibel, Director of the ZKM | Karlsruhe
Xavier Rey, Director of the Centre Pompidou, Paris
8:15 – 8:30 p.m. Improvisation on the piano
Hymn Controversy by Bardo Henning
8:30 p.m.
Curator guided tour of the exhibition
---
The exhibition will be open from 8 to 10 p.m.
The mint Café is also looking forward to your visit.
---
Matter. Non-Matter. Anti-Matter.
Past Exhibitions as Digital Experiences.
Sat, December 03, 2022 – Sun, April 23, 2023
The EU project »Beyond Matter: Cultural Heritage on the Verge of Virtual Reality« researches ways to reexperience past exhibitions using digital and spatial modeling methods. The exhibition »Matter. Non-Matter. Anti-Matter.« presents the current state of the research project at ZKM | Karlsruhe.
At the core of the event is the digital revival of the iconic exhibitions »Les Immatériaux« of the Centre Pompidou Paris in 1985 and »Iconoclash: Beyond the Image Wars in Science, Religion, and Art« of the ZKM | Karlsruhe in 2002.
Based on the case studies of »Les Immatériaux« (Centre Pompidou, 1985) and »Iconoclash: Beyond the Image Wars in Science, Religion, and Art« (ZKM, 2002), ZKM | Karlsruhe and the Centre Pompidou Paris investigate possibilities of reviving exhibitions through experiential methods of digital and spatial modeling. Central to this is also the question of the particular materiality of the digital.
At the heart of the Paris exhibition »Les Immatériaux« in the mid-1980s was the question of what impact new technologies and materials could have on artistic practice. When philosopher Jean-François Lyotard joined as cocurator, the project's focus eventually shifted to exploring the changes in the postmodern world that were driven by a flood of new technologies.
The exhibition »Iconoclash« at ZKM | Karlsruhe focused on the theme of representation and its multiple forms of expression, as well as the social turbulence it generates. As emphasized by curators Bruno Latour and Peter Weibel, the exhibition was not intended to be iconoclastic in its approach, but rather to present a synopsis of scholarly exhibits, documents, and artworks about iconoclasms – a thought experiment that took the form of an exhibition – a so-called »thought exhibition.«
»Matter. Non-Matter. Anti-Matter.« now presents in the 21st century the digital models of the two projects on the Immaterial Display, hardware that has been specially developed for exploring virtual exhibitions. On view are artworks and artifacts from the past exhibitions, as well as contemporary reflections and artworks created or expanded for this exhibition. These include works by Jeremy Bailey, damjanski, fabric|ch, Geraldine Juárez, Carolyn Kirschner, and Anne Le Troter that echo the 3D models of the two landmark exhibitions. They bear witness to the current digitization trend in the production, collection, and presentation of art.
Case studies and examples of the application of digital curatorial reconstruction techniques that were created as part of the Beyond Matter project complement the presentation.
The exhibition »Matter. Non-Matter. Anti-Matter.« is accompanied by an extensive program of events: A webinar series aimed at museum professionals and cultural practitioners will present examples of work in digital or hybrid museums; two workshops, coorganized with Andreas Broeckmann from Leuphana University Lüneburg, will focus on interdisciplinary curating and methods for researching historical exhibitions; workshops on »Performance-Oriented Design Methods for Audience Studies and Exhibition Evaluation« (PORe) will be held by Lily Díaz-Kommonen and Cvijeta Miljak from Aalto University.
After the exhibition ends at the ZKM, a new edition of »Matter. Non-Matter. Anti-Matter.« will be on view at the Centre Pompidou in Paris from May to July 2023.
>>>
Artists
Josef Albers, Giovanni Anselmo, Arman, Art & Language, Jeremy Bailey, Fiona Banner, DiMoDa featuring Banz & Bowinkel, Christiane Paul, Tamiko Thiel, Ricardo Miranda Zúñiga, Samuel Bianchini, Bio Design Lab (HfG Karlsruhe), Jean-Louis Boissier & Liliane Terrier, John Cage, Jacques-Élie Chabert & Camille Philibert, damjanski, Annet Dekker & Marialaura Ghidini & Gaia Tedone, Marcel Duchamp, fabric | ch, Eric J. Heller, Prof. Dr. Kai-Uwe Hemken (Art Studies Kunsthochschule Kassel / University of Kassel), Joasia Krysa, Leonardo Impett, Eva Cetinić, MetaObjects, Sui, Michel Jaffrennou, Geraldine Juárez, Martin Kippenberger, Carolyn Kirschner, Maria Klonaris & Katerina Thomadaki, Joseph Kosuth, Denis Laborde, Mark Lewis & Laura Mulvey, Kasimir Malevich, Pietro Manzoni, Gordon Matta-Clark, Peo Olsson, Katarina Sjögren, Jonas Williamsson, Roman Opalka, Nam June Paik, Readymades belong to everyone®, Jeffrey Shaw, Annegret Soltau, Daniel Soutif & Paule Zajderman, Klaus Staeck, Anne Le Troter, Manfred Wolff-Plottegg, Erwin Wurm
-
Curator
Livia Nolasco-RózsásCuratorial team
Felix Koberstein (ZKM)
Moritz Konrad (ZKM)
Marcella Lista (Centre Pompidou, Paris)
Philippe Bettinelli (Centre Pompidou, Paris)
Julie Champion (Centre Pompidou, Paris)Beyond Matter project team at ZKM
Marianne Schädler (managing editor)
Aurora Bertolli (communication)Exhibition team
Matthias Gommel (Scenography)
Janine Burger (Participation)
Thomas Schwab (Technical project management)Graphic design
AKU.coMuseum and Exhibition Technology
Martin Mangold - Organization / Institution
- Initiated by the ZKM | Center for Art and Media Karlsruhe and the Centre Pompidou, Paris, in collaboration with the Aalto University, Espoo, the Tallinn Art Hall, and the Tirana Art Lab.
>>>
Further locations and dates:
| Mar 14, 2022 – Mar 29, 2022 | Väre, Aalto University, Espoo |
| Apr 20, 2022 – Apr 25, 2022 | The Cube / Helsinki Central Library Oodi |
| Apr 25, 2022 – May 5, 2022 | Väre, Aalto University, Espoo |
| May 16, 2022 – May 22, 2022 | Design Museum Helsinki |
| June 25, 2022 – August 28, 2022 | Tirana Art Lab, Albanien |
| Dec 3, 2022 – Apr 23, 2023 | ZKM |
| Summer 2023 | Centre Pompidou, Paris |
---
Project
Cooperation partners
Supported by
Friday, November 25. 2022
Matter. Non-Matter. Anti-Matter Exhibition @ZKM | #digital #exhibition #iconoclash #immateriaux #zkm #beaubourg
Note:
An upcoming exhibition for fabric | ch, which will open next week at the ZKM in Karlsruhe.
We'll present a new work in this context (Atomized (re-)Staging), about which we'll hopefully find time to post some documentation on this blog later.
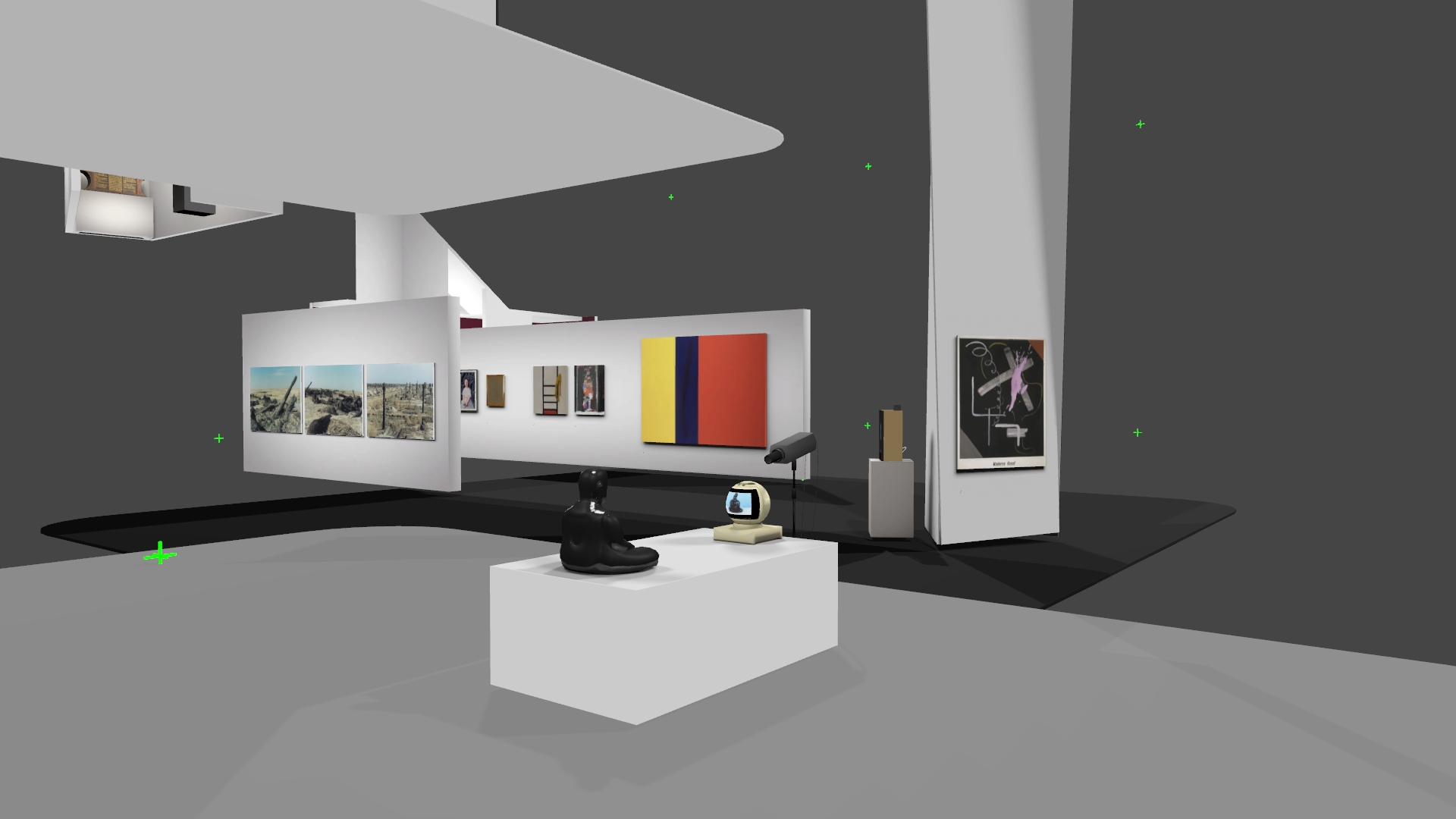

Via @beyondmatter
---
Matter. Non-Matter. Anti-Matter delves into the significance of digitality and computer-generated environments in the context of the material understanding of art production and the showcasing of it.
The exhibition presents the digital models of Les Immatériaux (Centre Pompidou, 1985) and Iconoclash. Beyond the Image Wars in Science, Religion, and Art (ZKM, 2002) on the newly developed Immaterial Display.
Furthermore, a selection of artworks and artifacts, mainly from the collections of the @centrepompidou and @zkmkarlsruhe, attest to a conceptual dematerialization and digital re-materialization of artworks.
---
Via @ptrckkllr
Friday, December 03. 2021
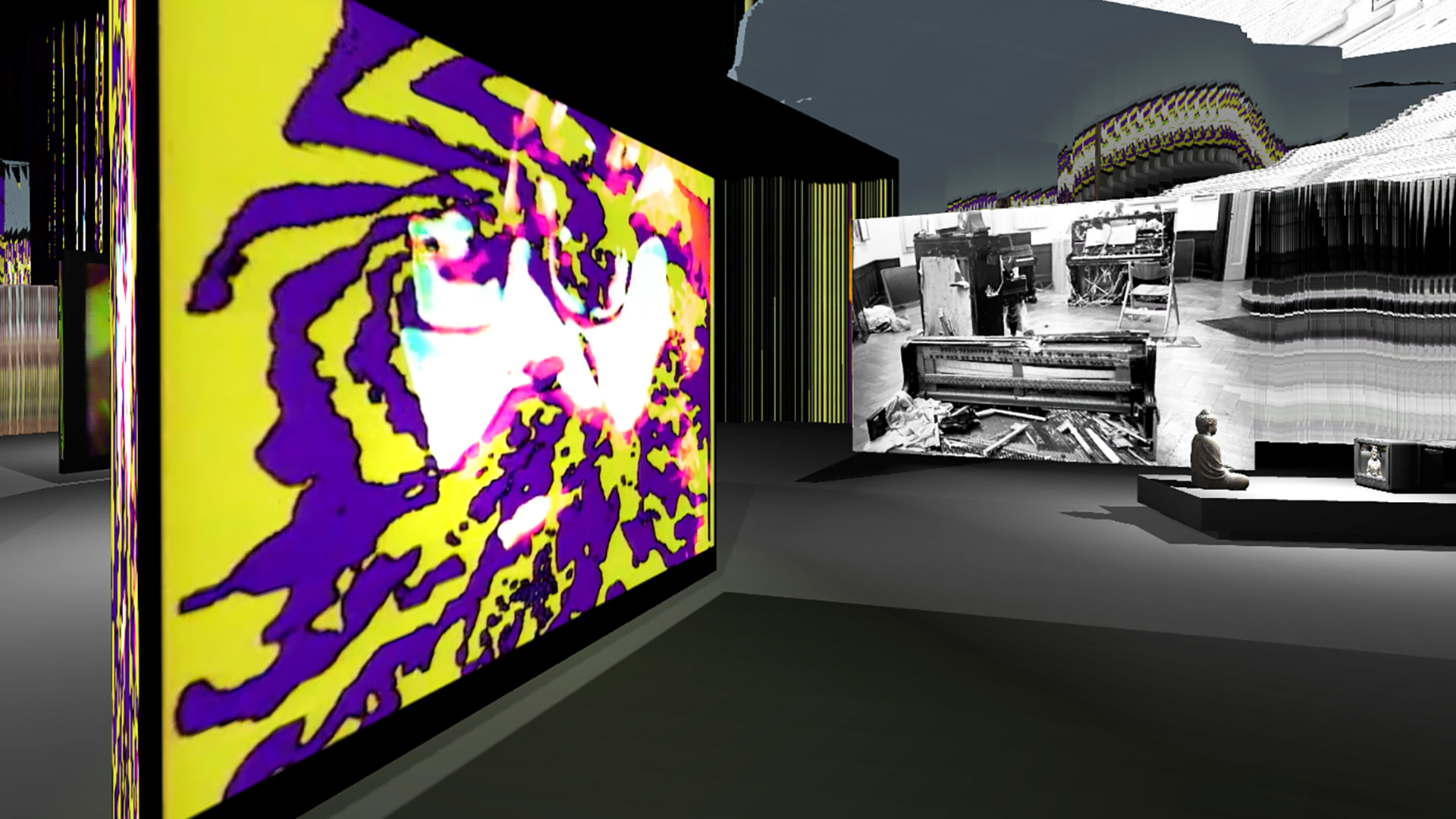
Atomized (*) Functioning by fabric | ch, digital Paik exhibition with Nam June Paik Art Center and ECAL | #paik #augmented #automated #exhibition
Note: We had the chance at fabric | ch to initiate a new research / project last Spring, in collaboration with the Nam June Paik Art Center (warning: long loading time!) in South Korea and ECAL / University of Art and Design Lausanne (HES-SO).
In this context, we're having the opportunity to work with some of the amazing material of the museum's collection and archive. It contains some of Paik's major works (single & multi-channel video in particular), that have been difficult to see since the passing of the artist, and most of its archives.
The museum indeed has the largest collection Paik's video, as well as some important installations and a large primary and secondary material about the production of the artworks themselves. The research undertaken is looking to give access to this material in new ways and forms, out of the physical museum and through digital means. For this task, we're planning to further dig into the archives and look at works that were realized, or not, during the Fluxus period ("Symphony for 20 Rooms", "Exhibition of Music, Electronic Television").
The aim of this research is to work on automated curating and digital display (likely AR) of exhibitions at anybody's place (home, appartment, office, warehouse, "garage", etc.), resonating with the concept of "Viewing Rooms" and therefore the title of this first phase of the research: (Re-)Viewing Paik. We are seeking forms of personal exhibitions, for specific spatial configurations and in which the artworks organize their presence themselves, according to an objective understanding of the space.
To achieve these research objectives, we'll work with fabric | ch's software and ongoing project that allows us to automate the creation of environments, based on sensors inputs: Atomized (*) Functioning (pdf), which is based on customizable/scriptable algorithmic and AI procedures. In the specific case of (Re-)Viewing Paik, it is used for curation and exhibition design purposes, therefore Atomized (curatorial) Functioning (pdf). Like we already did for this exhibition at HeK, in 2019.
-----
By fabric | ch
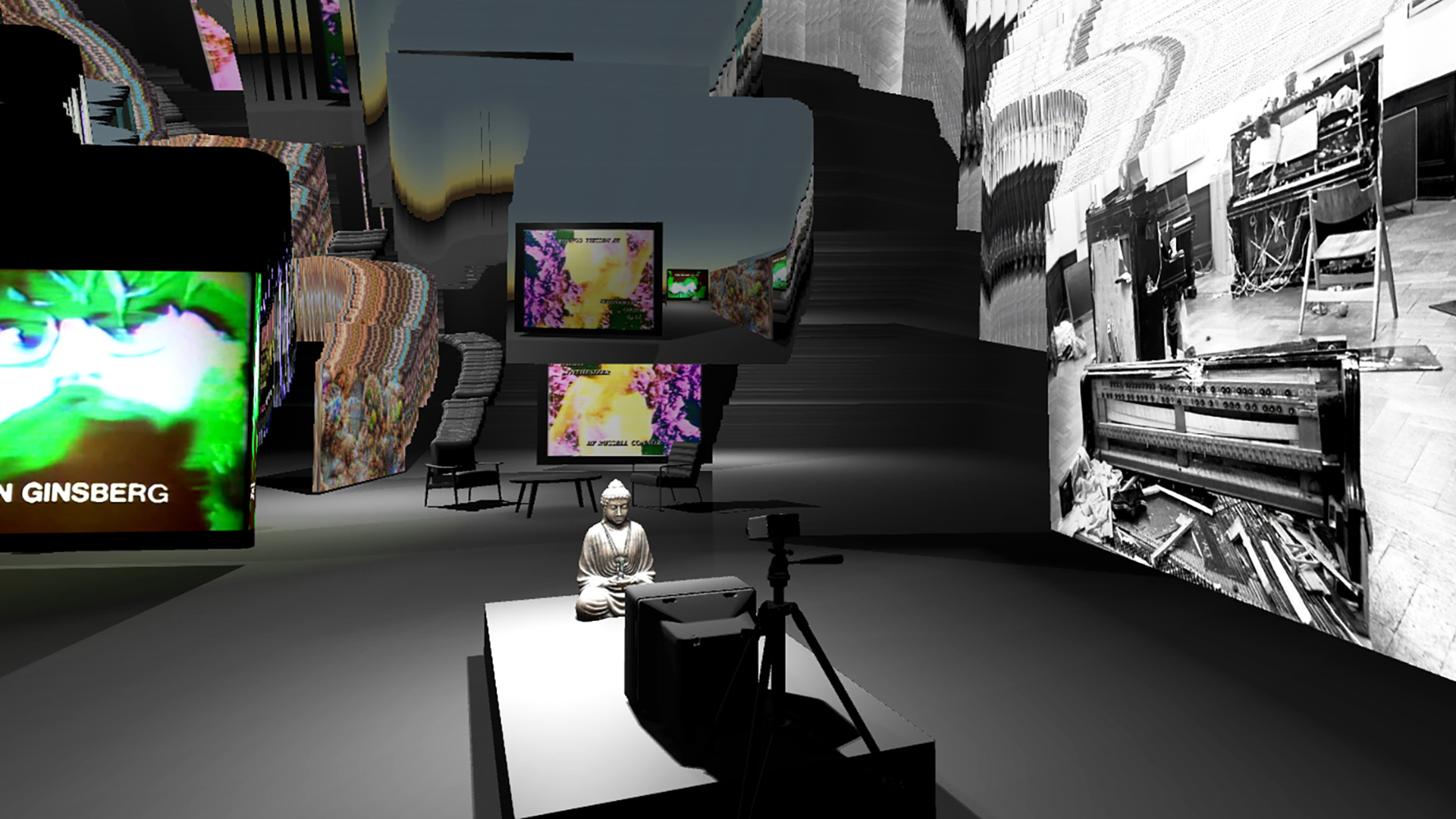
Below are early tests with a digital transposition/reconstruction of TV Buddha (literally), the zen media buddha in between a glitched and mirrored digital environment containing other artworks (video and photographies of the famous 1963 exhibition: Exposition of Music - Electronic Television).
This early phase of the work will see us work with the pieces selected by Nam June Paik Art Center curator and archivst Sans Ae Park. These pieces were selected mainly to test different artwork types and durations into their new display setup.
...
Friday, February 01. 2019
The Yoda of Silicon Valley | #NewYorkTimes #Algorithms
Note: Yet another dive into history of computer programming and algorithms, used for visual outputs ...
Via The New York Times (on Medium)
-----
By Siobhan Roberts

Donald Knuth at his home in Stanford, Calif. He is a notorious perfectionist and has offered to pay a reward to anyone who finds a mistake in any of his books. Photo: Brian Flaherty
For half a century, the Stanford computer scientist Donald Knuth, who bears a slight resemblance to Yoda — albeit standing 6-foot-4 and wearing glasses — has reigned as the spirit-guide of the algorithmic realm.
He is the author of “The Art of Computer Programming,” a continuing four-volume opus that is his life’s work. The first volume debuted in 1968, and the collected volumes (sold as a boxed set for about $250) were included by American Scientist in 2013 on its list of books that shaped the last century of science — alongside a special edition of “The Autobiography of Charles Darwin,” Tom Wolfe’s “The Right Stuff,” Rachel Carson’s “Silent Spring” and monographs by Albert Einstein, John von Neumann and Richard Feynman.
With more than one million copies in print, “The Art of Computer Programming” is the Bible of its field. “Like an actual bible, it is long and comprehensive; no other book is as comprehensive,” said Peter Norvig, a director of research at Google. After 652 pages, volume one closes with a blurb on the back cover from Bill Gates: “You should definitely send me a résumé if you can read the whole thing.”
The volume opens with an excerpt from “McCall’s Cookbook”:
Here is your book, the one your thousands of letters have asked us to publish. It has taken us years to do, checking and rechecking countless recipes to bring you only the best, only the interesting, only the perfect.
Inside are algorithms, the recipes that feed the digital age — although, as Dr.Knuth likes to point out, algorithms can also be found on Babylonian tablets from 3,800 years ago. He is an esteemed algorithmist; his name is attached to some of the field’s most important specimens, such as the Knuth-Morris-Pratt string-searching algorithm. Devised in 1970, it finds all occurrences of a given word or pattern of letters in a text — for instance, when you hit Command+F to search for a keyword in a document.
Now 80, Dr. Knuth usually dresses like the youthful geek he was when he embarked on this odyssey: long-sleeved T-shirt under a short-sleeved T-shirt, with jeans, at least at this time of year. In those early days, he worked close to the machine, writing “in the raw,” tinkering with the zeros and ones.
“Knuth made it clear that the system could actually be understood all the way down to the machine code level,” said Dr. Norvig. Nowadays, of course, with algorithms masterminding (and undermining) our very existence, the average programmer no longer has time to manipulate the binary muck, and works instead with hierarchies of abstraction, layers upon layers of code — and often with chains of code borrowed from code libraries. But an elite class of engineers occasionally still does the deep dive.
“Here at Google, sometimes we just throw stuff together,” Dr. Norvig said, during a meeting of the Google Trips team, in Mountain View, Calif. “But other times, if you’re serving billions of users, it’s important to do that efficiently. A 10-per-cent improvement in efficiency can work out to billions of dollars, and in order to get that last level of efficiency, you have to understand what’s going on all the way down.”
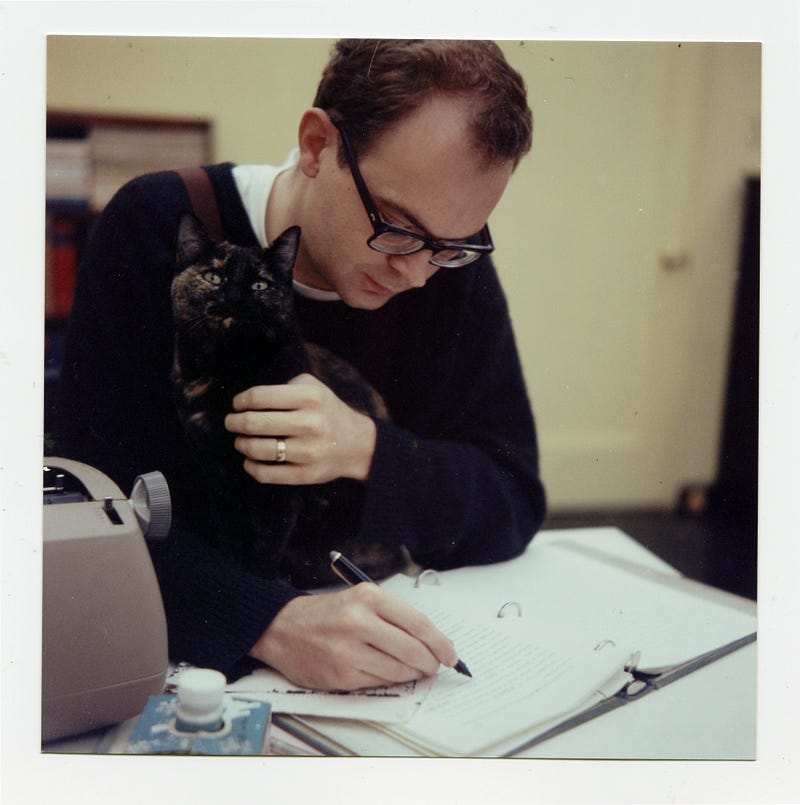

Dr. Knuth at the California Institute of Technology, where he received his Ph.D. in 1963. Photo: Jill Knuth
Or, as Andrei Broder, a distinguished scientist at Google and one of Dr. Knuth’s former graduate students, explained during the meeting: “We want to have some theoretical basis for what we’re doing. We don’t want a frivolous or sloppy or second-rate algorithm. We don’t want some other algorithmist to say, ‘You guys are morons.’”
The Google Trips app, created in 2016, is an “orienteering algorithm” that maps out a day’s worth of recommended touristy activities. The team was working on “maximizing the quality of the worst day” — for instance, avoiding sending the user back to the same neighborhood to see different sites. They drew inspiration from a 300-year-old algorithm by the Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler, who wanted to map a route through the Prussian city of Königsberg that would cross each of its seven bridges only once. Dr. Knuth addresses Euler’s classic problem in the first volume of his treatise. (He once applied Euler’s method in coding a computer-controlled sewing machine.)
Following Dr. Knuth’s doctrine helps to ward off moronry. He is known for introducing the notion of “literate programming,” emphasizing the importance of writing code that is readable by humans as well as computers — a notion that nowadays seems almost twee. Dr. Knuth has gone so far as to argue that some computer programs are, like Elizabeth Bishop’s poems and Philip Roth’s “American Pastoral,” works of literature worthy of a Pulitzer.
He is also a notorious perfectionist. Randall Munroe, the xkcd cartoonist and author of “Thing Explainer,” first learned about Dr. Knuth from computer-science people who mentioned the reward money Dr. Knuth pays to anyone who finds a mistake in any of his books. As Mr. Munroe recalled, “People talked about getting one of those checks as if it was computer science’s Nobel Prize.”
Dr. Knuth’s exacting standards, literary and otherwise, may explain why his life’s work is nowhere near done. He has a wager with Sergey Brin, the co-founder of Google and a former student (to use the term loosely), over whether Mr. Brin will finish his Ph.D. before Dr. Knuth concludes his opus.
The dawn of the algorithm
At age 19, Dr. Knuth published his first technical paper, “The Potrzebie System of Weights and Measures,” in Mad magazine. He became a computer scientist before the discipline existed, studying mathematics at what is now Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland. He looked at sample programs for the school’s IBM 650 mainframe, a decimal computer, and, noticing some inadequacies, rewrote the software as well as the textbook used in class. As a side project, he ran stats for the basketball team, writing a computer program that helped them win their league — and earned a segment by Walter Cronkite called “The Electronic Coach.”
During summer vacations, Dr. Knuth made more money than professors earned in a year by writing compilers. A compiler is like a translator, converting a high-level programming language (resembling algebra) to a lower-level one (sometimes arcane binary) and, ideally, improving it in the process. In computer science, “optimization” is truly an art, and this is articulated in another Knuthian proverb: “Premature optimization is the root of all evil.”
Eventually Dr. Knuth became a compiler himself, inadvertently founding a new field that he came to call the “analysis of algorithms.” A publisher hired him to write a book about compilers, but it evolved into a book collecting everything he knew about how to write for computers — a book about algorithms.
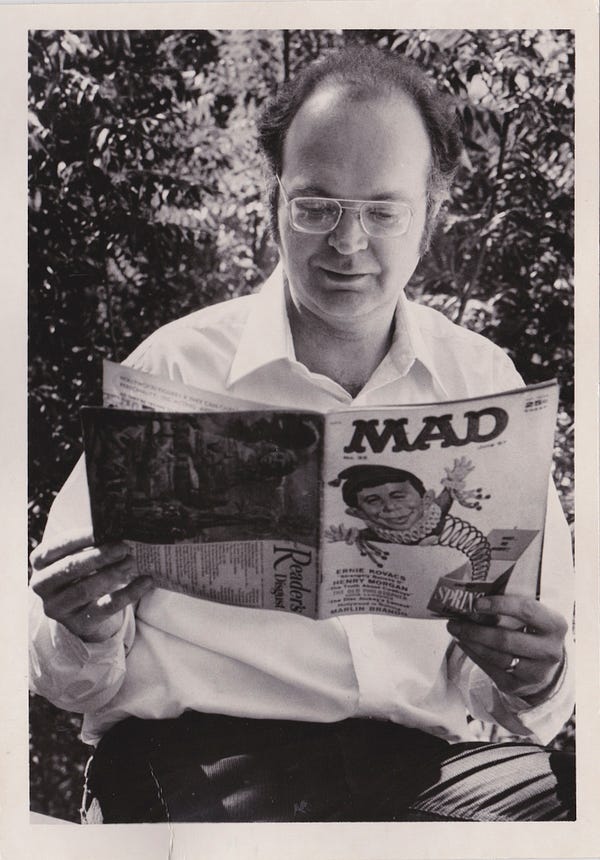
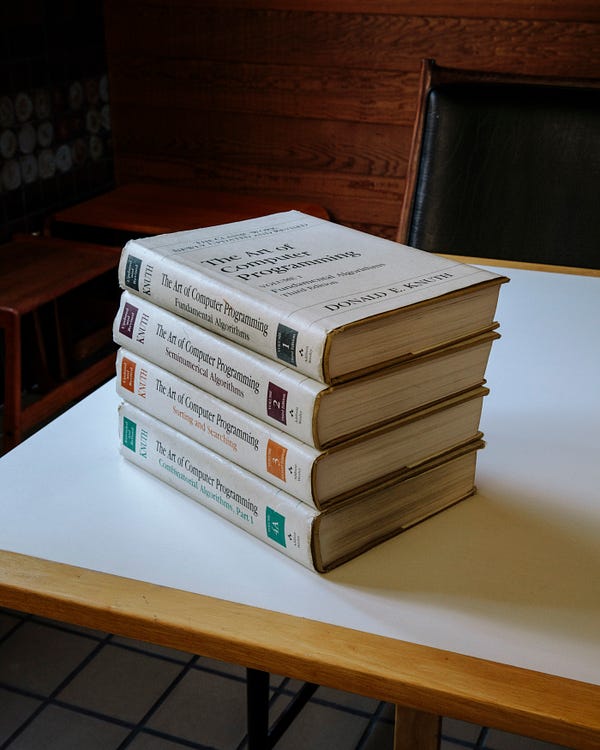


Left: Dr. Knuth in 1981, looking at the 1957 Mad magazine issue that contained his first technical article. He was 19 when it was published. Photo: Jill Knuth. Right: “The Art of Computer Programming,” volumes 1–4. “Send me a résumé if you can read the whole thing,” Bill Gates wrote in a blurb. Photo: Brian Flaherty
“By the time of the Renaissance, the origin of this word was in doubt,” it began. “And early linguists attempted to guess at its derivation by making combinations like algiros [painful] + arithmos [number].’” In fact, Dr. Knuth continued, the namesake is the 9th-century Persian textbook author Abū ‘Abd Allāh Muhammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī, Latinized as Algorithmi. Never one for half measures, Dr. Knuth went on a pilgrimage in 1979 to al-Khwārizmī’s ancestral homeland in Uzbekistan.
When Dr. Knuth started out, he intended to write a single work. Soon after, computer science underwent its Big Bang, so he reimagined and recast the project in seven volumes. Now he metes out sub-volumes, called fascicles. The next installation, “Volume 4, Fascicle 5,” covering, among other things, “backtracking” and “dancing links,” was meant to be published in time for Christmas. It is delayed until next April because he keeps finding more and more irresistible problems that he wants to present.
In order to optimize his chances of getting to the end, Dr. Knuth has long guarded his time. He retired at 55, restricted his public engagements and quit email (officially, at least). Andrei Broder recalled that time management was his professor’s defining characteristic even in the early 1980s.
Dr. Knuth typically held student appointments on Friday mornings, until he started spending his nights in the lab of John McCarthy, a founder of artificial intelligence, to get access to the computers when they were free. Horrified by what his beloved book looked like on the page with the advent of digital publishing, Dr. Knuth had gone on a mission to create the TeX computer typesetting system, which remains the gold standard for all forms of scientific communication and publication. Some consider it Dr. Knuth’s greatest contribution to the world, and the greatest contribution to typography since Gutenberg.
This decade-long detour took place back in the age when computers were shared among users and ran faster at night while most humans slept. So Dr. Knuth switched day into night, shifted his schedule by 12 hours and mapped his student appointments to Fridays from 8 p.m. to midnight. Dr. Broder recalled, “When I told my girlfriend that we can’t do anything Friday night because Friday night at 10 I have to meet with my adviser, she thought, ‘This is something that is so stupid it must be true.’”
When Knuth chooses to be physically present, however, he is 100-per-cent there in the moment. “It just makes you happy to be around him,” said Jennifer Chayes, a managing director of Microsoft Research. “He’s a maximum in the community. If you had an optimization function that was in some way a combination of warmth and depth, Don would be it.”
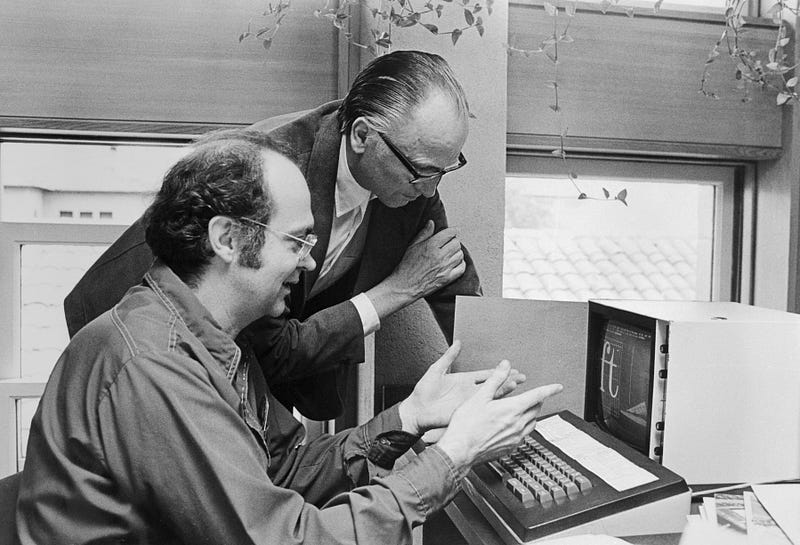

Dr. Knuth discussing typefaces with Hermann Zapf, the type designer. Many consider Dr. Knuth’s work on the TeX computer typesetting system to be the greatest contribution to typography since Gutenberg. Photo: Bettmann/Getty Images
Sunday with the algorithmist
Dr. Knuth lives in Stanford, and allowed for a Sunday visitor. That he spared an entire day was exceptional — usually his availability is “modulo nap time,” a sacred daily ritual from 1 p.m. to 4 p.m. He started early, at Palo Alto’s First Lutheran Church, where he delivered a Sunday school lesson to a standing-room-only crowd. Driving home, he got philosophical about mathematics.
“I’ll never know everything,” he said. “My life would be a lot worse if there was nothing I knew the answers about, and if there was nothing I didn’t know the answers about.” Then he offered a tour of his “California modern” house, which he and his wife, Jill, built in 1970. His office is littered with piles of U.S.B. sticks and adorned with Valentine’s Day heart art from Jill, a graphic designer. Most impressive is the music room, built around his custom-made, 812-pipe pipe organ. The day ended over beer at a puzzle party.
Puzzles and games — and penning a novella about surreal numbers, and composing a 90-minute multimedia musical pipe-dream, “Fantasia Apocalyptica” — are the sorts of things that really tickle him. One section of his book is titled, “Puzzles Versus the Real World.” He emailed an excerpt to the father-son team of Martin Demaine, an artist, and Erik Demaine, a computer scientist, both at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, because Dr. Knuth had included their “algorithmic puzzle fonts.”
“I was thrilled,” said Erik Demaine. “It’s an honor to be in the book.” He mentioned another Knuth quotation, which serves as the inspirational motto for the biannual “FUN with Algorithms” conference: “Pleasure has probably been the main goal all along.”
But then, Dr. Demaine said, the field went and got practical. Engineers and scientists and artists are teaming up to solve real-world problems — protein folding, robotics, airbags — using the Demaines’s mathematical origami designs for how to fold paper and linkages into different shapes.
Of course, all the algorithmic rigmarole is also causing real-world problems. Algorithms written by humans — tackling harder and harder problems, but producing code embedded with bugs and biases — are troubling enough. More worrisome, perhaps, are the algorithms that are not written by humans, algorithms written by the machine, as it learns.
Programmers still train the machine, and, crucially, feed it data. (Data is the new domain of biases and bugs, and here the bugs and biases are harder to find and fix). However, as Kevin Slavin, a research affiliate at M.I.T.’s Media Lab said, “We are now writing algorithms we cannot read. That makes this a unique moment in history, in that we are subject to ideas and actions and efforts by a set of physics that have human origins without human comprehension.” As Slavin has often noted, “It’s a bright future, if you’re an algorithm.”
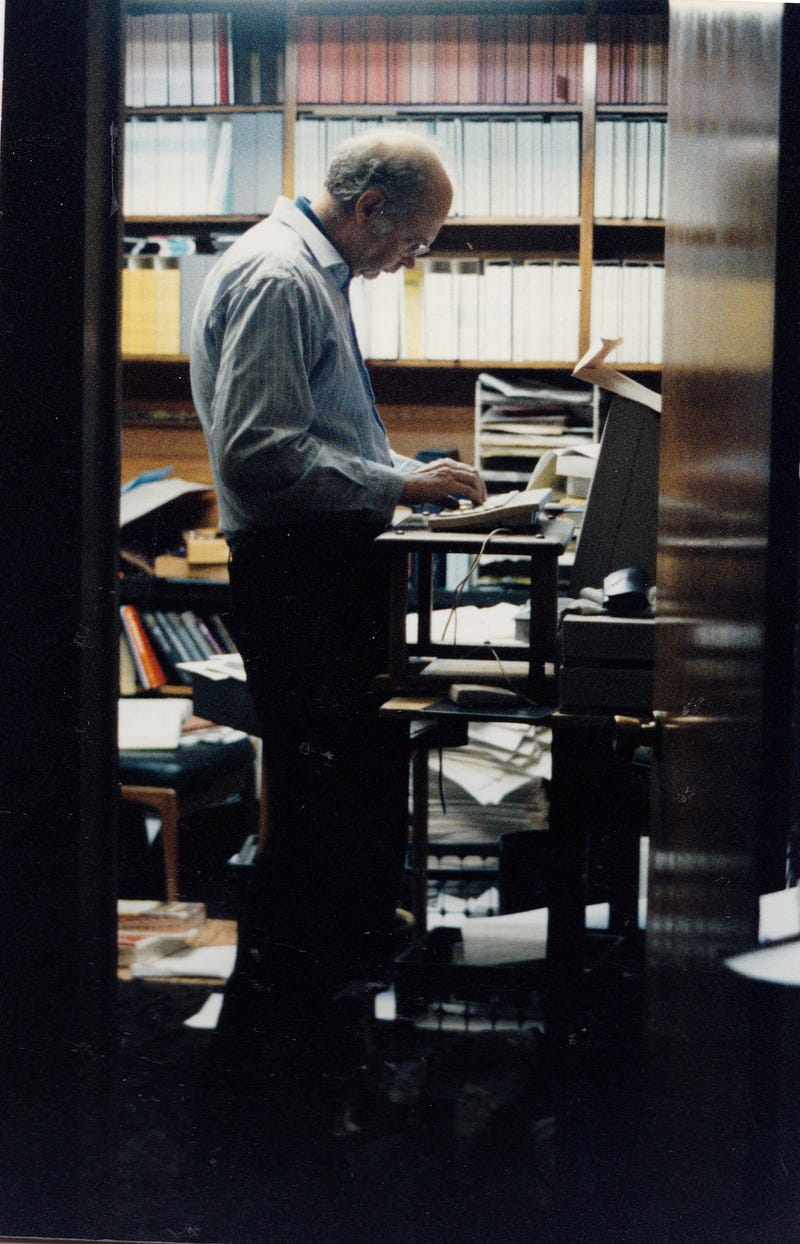

Dr. Knuth at his desk at home in 1999. Photo: Jill Knuth

A few notes. Photo: Brian Flaherty
All the more so if you’re an algorithm versed in Knuth. “Today, programmers use stuff that Knuth, and others, have done as components of their algorithms, and then they combine that together with all the other stuff they need,” said Google’s Dr. Norvig.
“With A.I., we have the same thing. It’s just that the combining-together part will be done automatically, based on the data, rather than based on a programmer’s work. You want A.I. to be able to combine components to get a good answer based on the data. But you have to decide what those components are. It could happen that each component is a page or chapter out of Knuth, because that’s the best possible way to do some task.”
Lucky, then, Dr. Knuth keeps at it. He figures it will take another 25 years to finish “The Art of Computer Programming,” although that time frame has been a constant since about 1980. Might the algorithm-writing algorithms get their own chapter, or maybe a page in the epilogue? “Definitely not,” said Dr. Knuth.
“I am worried that algorithms are getting too prominent in the world,” he added. “It started out that computer scientists were worried nobody was listening to us. Now I’m worried that too many people are listening.”
Thursday, November 22. 2018
Programmed: Rules, Codes, and Choreographies in Art, 1965–2018 | #algorithms #creation
Note: open since last September and seen here and there, this exhibition at the Withney about the uses of rules and code in art. It follows a similar exhibition - and historical as well - this year at the MOMA, Thinking Machines. This certainly demonstrates an increasing desire and interest in the historization of six decades - five in the context of this show - of "art & technologies" (not yet "design & technologies", while "architecture and digital" was done at the CCA).
Those six decades remained almost under the radar for long and there will be obviously a lot of work to do to write this epic!
Interesting in the context of the Whitney exhibition are the many sub-topics developed:
- Rule, Instruction, Algorithm: Ideas as Form /
- Rule, Instruction, Algorithm: Generative Measures /
- Rule, Instruction, Algorithm: Collapsing Instruction and Form /
- Signal, Sequence, Resolution: Image Resequenced /
- Signal, Sequence, Resolution: Liberating the Signal /
- Signal, Sequence, Resolution: Realities Encoded /
- Augmented Reality: Tamiko Thiel
Via Whitney Museum of American Art
-----
.jpg)
Programmed: Rules, Codes, and Choreographies in Art, 1965–2018 establishes connections between works of art based on instructions, spanning over fifty years of conceptual, video, and computational art. The pieces in the exhibition are all “programmed” using instructions, sets of rules, and code, but they also address the use of programming in their creation. The exhibition links two strands of artistic exploration: the first examines the program as instructions, rules, and algorithms with a focus on conceptual art practices and their emphasis on ideas as the driving force behind the art; the second strand engages with the use of instructions and algorithms to manipulate the TV program, its apparatus, and signals or image sequences. Featuring works drawn from the Whitney’s collection, Programmed looks back at predecessors of computational art and shows how the ideas addressed in those earlier works have evolved in contemporary artistic practices. At a time when our world is increasingly driven by automated systems, Programmed traces how rules and instructions in art have both responded to and been shaped by technologies, resulting in profound changes to our image culture.
The exhibition is organized by Christiane Paul, Adjunct Curator of Digital Art, and Carol Mancusi-Ungaro, Melva Bucksbaum Associate Director for Conservation and Research, with Clémence White, curatorial assistant.
fabric | rblg
This blog is the survey website of fabric | ch - studio for architecture, interaction and research.
We curate and reblog articles, researches, writings, exhibitions and projects that we notice and find interesting during our everyday practice and readings.
Most articles concern the intertwined fields of architecture, territory, art, interaction design, thinking and science. From time to time, we also publish documentation about our own work and research, immersed among these related resources and inspirations.
This website is used by fabric | ch as archive, references and resources. It is shared with all those interested in the same topics as we are, in the hope that they will also find valuable references and content in it.
Quicksearch
Categories
Calendar
|
|
July '25 | |||||
| Mon | Tue | Wed | Thu | Fri | Sat | Sun |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |||