Quicksearch
Thursday, July 07. 2011
An interview with Saskia Sassen about “Smart cities”
Preparing the Lift France 11 conference, and given our interest in a session about the future of cities, urban computing and its implications, we ran across this interesting column by Saskia Sassen about “Smart Cities” on a McKinsey digital. We liked it a lot and we invited her to the conference.
Few days ago, she kindly proposed to answer few questions I had about her perspective on this topic.
Nicolas: You recently wrote an essay about so-called “Smart Cities” at Mckinseydigital.com, I really liked your point about the need to “urbanize” the technologies deployed in Smart Cities projects. What do you mean by that and what do you think is missing in projects such as New Songdo or Masdar?
Saskia Sassen: This notion of urbanizing technology is one of several along those lines that I have been working out for a while. The starting point was not necessarily cities. It was the notion that in interactive domains the technology delivers its capabilities through ecologies that include non-technological variables –the social and the subjective, the logics/aims of users, for example finance uses the technology with different aims from Amnesty international, etc etc. Again, I make this argument for interactive domains, not, say, data pipelines.
There is another condition present in the interactive domain, separate from the technology itself. At the beginning I studied how the logic of finance (a sector that is deeply embedded in digital networks and digitized spaces) is not the logic of the engineer and computer scientist and software developer who made the digital domain. The effect is that the user (finance) does not necessarily use all the properties that the engineer etc. put into it. I also looked at civil society organizations along the same lines. This helps explain why the outcomes never correspond to what we may have predicted based on the capacities of the technology.
Now I am looking at cities through the same lens. Users bring their own logics to these technologies. In the case of a city with its vast diversities of people and what makes them tick, the outcome can be quite different from what the designers expected. And this matters. This keeps the city alive, and open. When you embed interactive technologies in urban settings, it is important to allow for this mutating as diverse types of users bring their own logics to those technologies. If the technology controls all outcomes in a routinized fashion ((as if it were a data pipeline) there is a high risk that it will become obsolete, or less and less used, or so routinized that it barely is interactive. More like buying a ticket from an automaton: yes you have choices, but you can hardly call this interactive.
The key, difficult, and ever changing question is how do we keep technologies open, responsive to environmental signals and to users choices, including what may seem quirky from the perspective of the engineer. The city is full of signals and quirky uses: given a chance , it would urbanize a whole range of technologies. But this possibility needs to be made – it is not simply a function of interactive technologies as we know them now, and it needs to go beyond the embedded feedback capability. Open Source is more like it.
Nicolas: Do you feel that networked technologies can lead to new forms of urbanity? Said differently, to what extent are the cities of the future shaped by our past urban experiences and infrastructures?
Saskia Sassen: Urbanity is a mutant. And this means it is made and remade along many different concepts/ideas/imaginations across the world. It can happen in sites where we, we of our westernized culture, might not see it. At night in working class neighborhoods of Shanghai bus stops become public spaces –that is urbanity. In some megacities the only spaces that the poor, often homeless have, are what during daytime hours we see as infrastructure: spaces where multiple bus lines intersect or end in. There are many many such examples of practices that destabilize the formal meaning of a space: this, again, takes making, and in that making lies an urbanity. I do think that urbanity is made; it is not only beautifully designed urban settings.
So yes! I think that networked technologies will also, and in fact, already are, leading to new forms of urbanity. The most familiar of these are of course using the tech to communicate about swarming an actual space –a square, a furniture shop—and diverse locational devices. Again, what intrigues me is to think beyond these somewhat “pre-scribed” possibilities: in two ways. One is through the unsettling, making unstable, the prescribed options embedded in the technology’s design. For instance, inserting a given technological capability into a different ecology of elements (in the sense I used this earlier –technical and non-technical elements). This is what hackers do, in a way. In the case of the city, it would mean bringing an urban logic into that ecology –the city as the hacker. .. a benign, positive hacker of a range of technological domains in cities. The other is what I like to refer to as “barefoot engineering” — this resonates with the so-called “barefoot doctors” in China’s villages during Communism –knowledgeable locals who knew the properties of plants and understood the village. We need urban “barefoot engineers”!
Nicolas: In the aforementioned paper, you use the term “open-source urbanism”. It’s interesting to see that metaphor coming from digital culture are currently transposed beyond their original realms. How do you think the “open source” concept can be applied to urbanism? What would be the limits and opportunities?
Saskia Sassen: As a technological practice of innovation, Open Source has not been about cities, but about the technology itself. Yet it resonates with what cities have and are at ground-level, where its users are. The park is made not only with the hardware of trees and ponds, but also with the software of people’s practices. There are manay examples, and each city has its own. In my city, NY, an example of such people’s software is New York’s Riverside Park in the 1980s which went from being a no-go zone, charged with dangers, to being a park for all those who wanted to use it. How did this switch happen? In part because dog-owners started to walk their dogs in large numbers. Having a dog was itself a function of feeling insecure in a city of high murder rates and much mugging. But the city as lived mutating environment allowed people to talk back: get a dog, walk your dog, go in groups, and you recover the territory of the park. Another example is the recent proliferation of urban agriculture; it was not a top-down decision. It resulted from a mix of conditions, primarily the desire of city residents to make, to green, to transform, and the romance with fresh produce. And now the push is for every roof, every empty plot of land to become a site for urban agriculture. Here we see that a thousand individual decisions created an urban possibility and transformation. There are many diverse initiatives that produce these kinds of “third space.”
These are ways in which the city can talk back. We can think of the multiple ways in which the city talks back as a type of open-source urbanism: the city as partly made through a myriad of interventions and little changes from the ground up. Each of these multiple small interventions may not look like much, but together they give added meaning to the notion of the incompleteness of cities and that this incompleteness gives cities their long lives, their flexibility, their capacity to mutate. And this potential for distributed outcomes is a natural for open source technology. But beyond the technology proper, bringing open source concepts into multiple urban settings/domains strengthens these core features of cities, make them cities of people, strengthen the rights to the city.
In sharp contrast, I think that the model of “intelligent cities” as propounded by technologists, with the telepresence efforts of Cisco Systems a key ingredient, misses this opportunity to urbanize the technologies they mobilize. Secondly, the intelligent city concept if too rigid, becomes a futile effort to eliminate the incompleteness of the city, to get full closure/control. This is a recipe for built-in obsoleteness. Imagine if Rome could not have mutated across the millennia: it would be a dead city now. Third, the planners of intelligent cities, notably Songdo in South Korea actually make these technologies invisible, and hence put them in command rather than in dialogue with users.
Beyond the imagery of open-source urbanisms, can we strengthen this positive scenario of the city’s incompleteness by actually deploying open-source technologies in a variety of urban contexts
Related Links:
Monday, April 04. 2011
Saskia Sassen to keynote Lift France '11
Via Lift via Contemporary Spaces
-----

When one of the world's prominent thinker about global thinking takes a look at "smart cities", the result differs from what most of the Industry tends to say - and that's why we like it:
"I have long thought that all the major infrastructures in a city—from sewage to electricity and broadband—should be encased in transparent walls and floors at certain crossroads, such as bus stops or public squares. If you can actually see it all, you can get engaged. Today, when walls are pregnant with software, why not make this visible? (...) The challenge for intelligent cities is to urbanize the technologies they deploy, to make them responsive and available to the people whose lives they affect. Today, the tendency is to make them invisible, hiding them beneath platforms or behind walls—hence putting them in command rather than in dialogue with users. One effect will be to reduce the possibility that intelligent cities can promote open-source urbanism, and that is a pity. It will cut their lives short. They will become obsolete sooner. Urbanizing these intelligent cities would help them live longer because they would be open systems, subject to ongoing changes and innovations. After all, that ability to adapt is how our good old cities have outlived the rise and fall of kingdoms, republics, and corporations."
Cities are the places where Lift France '11's five key topics (OPEN, CARE, GREEN, LEARN, SLOW) will congregate. We're therefore especially happy that Saskia Sassen has agreed to give the opening speech.
Related Links:
Wednesday, March 16. 2011
Aerotropolis: An Interview with Greg Lindsay
Via BLDGBLOG
-----
by noreply@blogger.com (Geoff Manaugh)
In his book London Orbital, Iain Sinclair writes that Heathrow Airport—with its "inscrutable geometry," surrounded by "international hotels, storage facilities, [and] semi-private roads"—is utterly "detached from the shabby entropy" of London. Indeed, "Heathrow is its own city, a Vatican of the western suburbs."
 If Atlanta's Hartsfield-Jackson International Airport were to become its own country, its annual workforce and user base would make it "the twelfth most populous nation on Earth," as John Kasarda and Greg Lindsey explain in Aerotropolis; even today, it is the largest employer in the state of Georgia.
If Atlanta's Hartsfield-Jackson International Airport were to become its own country, its annual workforce and user base would make it "the twelfth most populous nation on Earth," as John Kasarda and Greg Lindsey explain in Aerotropolis; even today, it is the largest employer in the state of Georgia.
As J.G. Ballard once wrote, and as is quoted on the frontispiece of Aerotropolis:
- I suspect that the airport will be the true city of the 21st century. The great airports are already the suburbs of an invisible world capital, a virtual metropolis whose fauborgs are named Heathrow, Kennedy, Charles de Gaulle, Nagoya, a centripetal city whose population forever circles its notional center, and will never need to gain access to its dark heart.
The world of the aerotropolis is a world of instant cities—urbanization-on-demand—where nations like China and Saudi Arabia can simply "roll out cities" one after the other. "Each will be built faster, better, and more cheaply than the ones that came before," Aerotropolis suggests: whole cities created by the warehousing demands of international shipping firms. In fact, they are "cities that shipping and handling built," Lindsay and Kasarda quip—urbanism in the age of Amazon Prime.
The world of the aerotropolis, then, is a world where "a metropolitan area's position in the airline network determine[s] its employment growth and not, as commonly supposed, the other way around." Or, as a representative from FedEx explains to Greg Lindsay, "Not every great city will be an aerotropolis, but those cities which are an aerotropolis will be great ones."
Surely, though, this kind of breathless rhetoric is a reliable sign of hype. What are the real political and economic conditions of the aerotropolis; what transformations might it undergo in an age of peak oil and climate change; and who, in the end, will actually live there and manage it? This latter question seems particularly urgent: does the aerotropolis represent the culmination of the city's slow depoliticization—an urban form without mayors or democracy—run instead by a managerial class of logistics professionals and CFOs?
Or do these very questions reveal a misconception about what the aerotropolis is and will be?
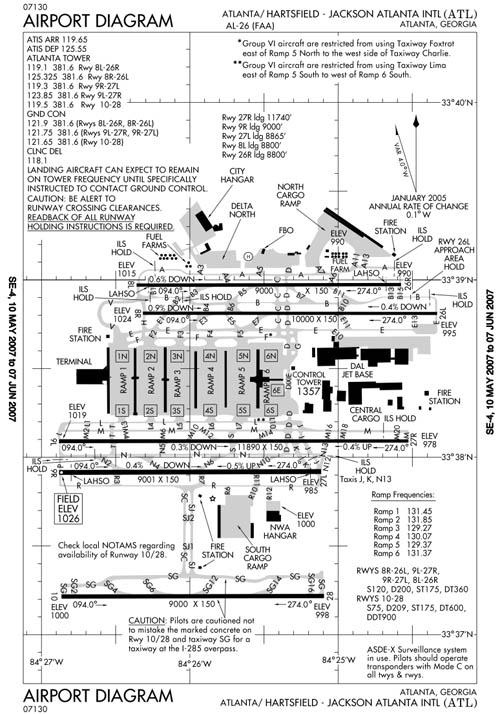 [Image: A plan of Atlanta's Hartsfield-Jackson Airport, via Wikipedia].
[Image: A plan of Atlanta's Hartsfield-Jackson Airport, via Wikipedia]. To begin to answer these questions, and in preparation for a live interview that will take place in Los Angeles on Tuesday, April 5, at the A+D Museum, I spoke to Aerotropolis co-author Greg Lindsay about these and many other topics, from the aerotropolis itself to instant cities, the appeal of the urban realm for today's technology firms, and metropolitan futurism circa Le Corbusier. The resulting conversation, included below, shows Lindsay to be both frank and refreshingly candid about the book. He is also someone clearly excited to talk about the future of the city, aerotropolis or not: simply to transcribe this interview, I had to slow the audio file down to nearly 85% of its original speed just to unpack Lindsay's jet stream of ideas and references.
Consider this a teaser, then, for the event on April 5. Until that time, pick up a copy of Kasarda's and Lindsay's book to see what you think; and, if you get a chance, take a look at the second half of this conversation, during which the tables are turned and Lindsay interviews me for Work in Progress, the newsletter of Farrar, Straus and Giroux. There, we discuss the role of the architect in a world of smart cities and instant urbanism, the fate of criticism in the context of architecture blogs, and where we might turn next for tomorrow's spatial ideas.
BLDGBLOG: Let’s start with the most basic question of all: what is an aerotropolis?
Greg Lindsay: John Kasarda, of the University of North Carolina, came up with the idea twenty years ago—though, in researching the book, I found that word’s original appearance in print was actually in Rem Koolhaas’s Great Leap Forward, quoting a local Chinese official. Kasarda first heard it in China, as well.
In terms of vision, I think there are really two definitions of it, depending on which of the two authors you speak to—Kasarda or myself.
Kasarda’s notion of an aerotropolis is basically a city or a region planned around an airport. In his mind’s eye, everything is spatially divided by usage: hangars, cargo terminals, office parks, business hotels, six-lane highways, merchandise marts. There’s no real urban form at all. On one level, it’s like Edge City: the form is dictated by development money and the respective need for access to the airport at the center. But, on another, the design is glossed over or left out. In models and renderings, they never achieve a resolution above little white boxes.
He sees the aerotropolis purely in terms of time/cost equations. Density and design is secondary. A layperson would describe it as sprawl. It’s an urban vision without any real urbanity.
Then there’s my definition of it—and I think I take a broader view. I would describe the aerotropolis as any city that has a closer relationship to the air, and to other cities accessible through the air, than to its immediate hinterlands. It’s a city that was basically invented because of the necessities of air travel.
Dubai, to me, is a perfect example of that. Thirty years ago, of course, there was nothing there; Dubai had little oil and even fewer people. But, basically through sheer will, it used its airport and its airline, Emirates, to build itself into a hub. It transformed itself legally and regulatory-wise, and made itself the freezone of the Middle East—and the pleasure den, and all the things it’s become.
Dubai’s also interesting because it illustrates the grander vision of the book, which is that transportation always defines the shape and look of cities. Joel Garreau made this point twenty years ago, that cities are defined by the state of the art of transportation at the time. I think many of the cities we love today are classic railroad cities—such as New York, built around Grand Central Station, and Chicago, where the first skyscrapers sprang up across the street from the Illinois Central’s railyard.
But the idea now is: if you’re building a city from scratch in the middle of China or India, then you’re building it around an airport. The airport is the city’s economic reason for being. You’re trying to connect to a global economy, starting from zero.
Dubai is interesting in that regard. Nobody really understood what Dubai was about, or what they were trying to do there, but its plans make sense if you look at it from the perspective that there’s this theoretical population all dispersed across the Middle East and southeast Asia, and they’re all flying in to use the city in bits at a time.
The notion of the aerotropolis, then, is basically that air travel is what globalization looks like in urban form. It is about flows of people and goods and capital, and it implies that to be connected to a city on the far side of the world matters more than to be connected to your immediate region. The aerotropolis spatializes what people like Saskia Sassen have been writing about for twenty years in books like The Global City.
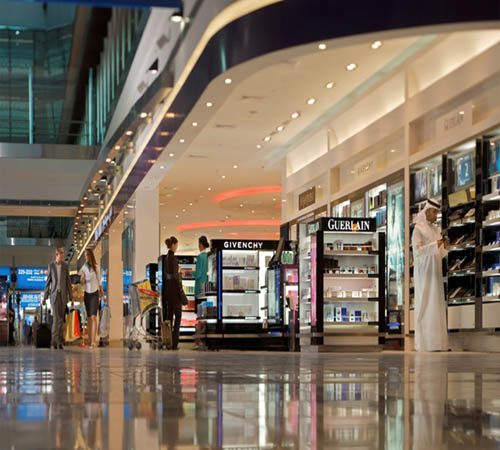
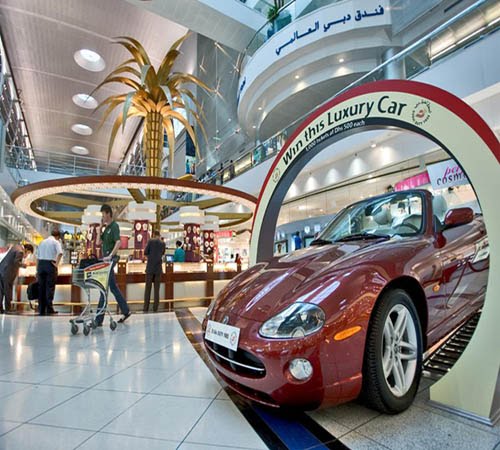

 [Images: Dubai International Airport promotional images; vertical distortion is in the originals. Courtesy of the Dubai International Airport Media Center].
[Images: Dubai International Airport promotional images; vertical distortion is in the originals. Courtesy of the Dubai International Airport Media Center]. BLDGBLOG: I’m curious about the political requirements for making an aerotropolis happen. On the level of regulation, zoning, and so on, what needs to occur for an aerotropolis to become realizable?
Lindsay: Well, I always say that we built our airports in the United States before we knew what they were for. We didn’t really understand the scale of future operations or the geographic footprint they would need, so we built them within footprints that were never going to be sustainable for the levels of traffic they would ultimately absorb.
So we ended up with places like LAX. One of the things I love noting is that, when LAX was first built, it was criticized because the field was seen as too far from downtown—whereas, today, you have an airport that’s basically landlocked on all sides, and has been for almost fifty years. This puts LAX and Los Angeles in an intractable situation, considering the economics of air travel, which require concentration for hubbing, for operational efficiency, for all of that. It’s in the best interests of an airline to concentrate in one place—and LAX is a place that just cannot expand.
The next stage is understanding the scale you need to operate on: you need to plan for a larger region. We talk about regional planning in the United States, but we do so little of it. We hardly even understand how economies cross what are almost arbitrary borders at this point, between counties and cities. I had difficulty finding reliable gross metropolitan product numbers, and Richard Florida had to go so far as to measure light pollution from space in one of his books.
In Los Angeles, because of the failure of Orange County to build a second airport, if you’re going to fly internationally, and if you’re basically anywhere from Malibu to the Mexico border, you’re going to pass through LAX—which is a hell of a catchment area and an incredible strain to put on one airport. That’s partly due to when Orange County tried to build an airport at the former El Toro Marine base and ended up in a bizarre civil war: you had the right-leaning NIMBY interests on the side of the environmentalists, and you had the Chamber of Commerce siding with the poor immigrants of Orange County, because they wanted the jobs. It made for this schizoid conflict.
To continue from a narrow American perspective, I think the examples of Memphis and Louisville are fascinating, where the sheer economic force of FedEx and UPS basically willed them into being.
Those cities used to be river-trading towns—cotton and tobacco, respectively—before they became basically southern rustbelt towns. But then, in the 1970s and 80s, they were reborn as company towns of FedEx and UPS. In a sense, their economics—for better or for worse, and that’s very much up for debate—are held hostage by our e-commerce habits: every time we press the one-click button on Amazon, it leads to this gigantic logistical mechanism which, in turn, has led to the creation of vast warehouse districts around the airports of these two cities.
One of the things I tried to touch on in the book is that even actions we think of as primarily virtual lead to the creation of gigantic physical systems and superstructures without us even knowing it.
 [Images: Laser-guided FedEx hub urbanism at work; all images courtesy of FedEx. Meanwhile, it is about UPS—not FedEx—but John McPhee's essay "Out in the Sort" is a minor classic in what I might call the logistical humanities].
[Images: Laser-guided FedEx hub urbanism at work; all images courtesy of FedEx. Meanwhile, it is about UPS—not FedEx—but John McPhee's essay "Out in the Sort" is a minor classic in what I might call the logistical humanities].BLDGBLOG: In this context, you point out in the book that Kasarda “proposes building cities by corporations for corporations, guaranteeing their survival by tailoring them to clients’ specifications—beginning with the airport.” The city is not an expression of human culture, so to speak, but a kind of 3-dimensional graph of economic activity.
Lindsay: Yes, the aerotropolis—as Kasarda preaches it and as has been implemented in places like Dubai and elsewhere—is less about urbanity than repurposing the city as a “machine for living,” to quote Le Corbusier.
The aerotropolis is basically an economic engine. Planners are looking for ways to make these cities as frictionless as possible in terms of doing business—which means that, in places like Dubai, the tax-free zones and enclaves such as Dubai Media City and Dubai Internet City and the Jebel Ali Free Zone can basically wage an economic war of all against all when it comes to competing cities. They were designed as weapons for fighting trade wars, and their charter—to be duty-free and hyper-efficient—reflects this. So it’s interesting in the sense that these cities are infrastructure-as-weaponry, which Rem Koolhaas wrote about in “The Generic City” [PDF]—“City X builds an airport to kill City Y.” They’re competing rather than complementing.
China’s cities, in particular, are building infrastructure not as a way to improve urban living across these larger regions, but basically so that they can do battle against one another for attention and investment.
BLDGBLOG: Sticking with Dubai, at one point you write: “High-functioning dictatorships such as Dubai’s don’t faze [Kasarda]. If anything, they’re the only ones who move fast enough.” This sounds quite ominous. In some ways, I’m reminded of recent architectural debates in which people seemed to side either with a revival of Jane Jacobs or with a revival of Robert Moses—where the latter camp claims that what we really need now is a kind of infrastructural dictator, someone who will get the job done, whether that’s high-speed rail or a new tunnel between New Jersey and Manhattan. But what are the political implications of the aerotropolis—and is a “high-functioning dictatorship” really the most appropriate form of government for such a city?
Lindsay: Well, it’s obvious if you look at the projects under way that a great many of them are being realized by authoritarian governments, whether that’s China or the Middle East monarchies.
Basically, the aerotropolis, or any kind of instant city project, seems to be enabled by autocracy. That’s the case whether you’re building an aerotropolis in Dubai or whether you’re building one in Beijing, or whether you’re building smart cities in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Arabia is building six “economic cities,” quote-unquote, which will double as aerotropoli. The Saudis are trying to revamp their whole air system, develop their national airline, and then also make these smart cites into job magnets, thinking that they could basically build a society from scratch.
It’s funny that you’d mention Robert Moses, though, because I didn’t even really think of him in the context of this book. It’s gone beyond the scale of Moses. Moses was a regional planner operating in what is ultimately a democratic government. But you have planners—in fact, you have technocrats—who are commissioning and building whole cities now. I think Robert Moses would be a fantastic figure today—because he would be a vast improvement over some of the secret decisions being made in China over what they’re going to build, where, and to what end.
This goes back to what I was saying about the war between cities. I was reading a description by Steven Cheung, a Chicago School economist who taught in Hong Kong. He presented a paper in Beijing in 2008 that was partially translated in Richard McGregor’s The Party, where he discusses the economic model that has driven China. His notion is that every city there is at total war with each other economically, in order to attract foreign investment. They’ll promise you everything, and they’ll move as fast as possible, and they’ll build whatever you need to make it happen. And that’s the same impulse behind the people who are building aerotropoli. You end up with a city like Chongqing, with 32 million people, where they’re building a massive new airport that will create hundreds of thousands of new jobs for the millions of people who were displaced by the Three Gorges Dam.
On some level, I think in America we don’t even understand the level and the pace of change that is happening in China, where, because of decisions made by central planners, millions of people are being urbanized—literally at the flip of a switch, because they’re simply changing their legal status from “rural” to “urban.” Suddenly, three million farmers turn into three million urbanites, and now you have to find jobs for them, and situate them, and do all these things.
For an autocrat, it’s easy to will that into existence—and the pleasures of doing so are well known. I mean, Thomas Friedman in Hot, Flat, and Crowded has a whole section on “if only we could be China just for one day…”
In terms of the aerotropolis, maybe the most interesting developments will be in India. They intend to build, I don’t know, a hundred airports from scratch, and they are actively planning a few in the mold of Kasarda’s aerotropoli. And considering India is a democracy, it’s led to some massive political battles. They’re fighting over the land; they’re fighting over whether to build one above coalfields. It will be very interesting to see at what rapidity they can move forward with a true democratic process.
But I think the classic example in the book is in Thailand, where Kasarda has been a teacher and government advisor for years and where he sold his vision of the aerotropolis to Thaksin Shinawatra—who was then the elected prime minister but was almost universally considered an oligarch. People who were involved in that process are still unsure that Thaksin ever understood what Kasarda was trying to tell him, or whether Thaksin simply saw it as a land grab—a way to install his own family members in development companies and reap huge profits from it.
The flipside is Dubai. They screwed up a lot of things there but, through several generations of rulers now, they’ve understood that investing in infrastructure and investing in trade was the key to long-term success.
 [Image: The now-erased runways of Denver's old Stapleton Airport; the airfield has since become a New Urbanist residential development. Photo courtesy of the Colorado Department of Transportation].
[Image: The now-erased runways of Denver's old Stapleton Airport; the airfield has since become a New Urbanist residential development. Photo courtesy of the Colorado Department of Transportation].BLDGBLOG: A few times now, you’ve mentioned the prospect of a failed aerotropolis—or at least an aerotropolis that is incorrectly implemented. I’m really curious about that—about what might happen to an aerotropolis if the growth of air freight and business travel doesn’t actually pan out as expected. In the book, you do touch on things like climate change and peak oil—but is it short-sighted, in a way, to build cities specifically around one form of transportation, one that might someday prove inaccessible?
Lindsay: In terms of building a city around an airport, there’s a common misconception that we’ll be building homes right up to the fence of the airport. But the airports we build today are massive, and they have huge noise buffers around them, which isn’t the case at older airports. Denver’s old Stapleton Airport is a classic example of this, where people actually did live a couple hundred yards away from the runways, with all of the piercing noise. But when they built the new Denver International out beyond the city, it’s two miles from the runway to the border of the airport, and it floats on this sea of grass that nothing can ever get close to—though developers are trying.
So, even though you’ll have fast access to the airport, it’s not like you’re going to look across the street and see planes landing. Then again, I live in brownstone Brooklyn under a flight path, eight miles from LaGuardia, and, on rainy nights, it sounds like planes are about to land on my desk. It’s all relative.
As for peak oil and climate change, I devoted a whole chapter to them in the book. I believe wholeheartedly in peak oil—you simply cannot geometrically increase consumption of a finite resource—but I do believe that biofuels, likely harvested from micro-organism production platforms, can produce sustainable, replenishable jet fuel. The science is sound; the scale of production is what’s in question.
But even if you think climate change is inescapable, or that peak oil will do us in first, and even if you think that aviation will go away and that globalization will stop, for good or for bad—but probably for good—to me, the question is: Are you willing to bet the future on that?
Because what’s interesting to me is that, in China, India, and the Middle East—and anywhere else in the developing world whose cities have been cut out of globalization so far—they’re building these cities to connect themselves to the global economy, in which they intend to participate, if not someday to dominate.
The more unsettling question that I wanted to raise in this book—rather than just cheerlead for airport cities, as some critics have accused me of doing—is ask whether we need to do the same to keep pace. Do we need to build or re-build our cities to more efficiently process goods and people? Or will these places collapse under their own weight?
In China, the answer may be both. But this is the world we made—one-click shopping creating giant hubs in Louisville and Memphis—and this the world they’re making. It may end in disaster, or it could lift hundreds of millions of people out of poverty—and hurt our own economy further in the process.
These are questions I wanted to leave to the reader. The reasons autocracies are so eager to embrace an aerotropolis or an instant city is because they’re willing basically to throw money and people at the problem in an attempt to catch up to us in an incredibly rapid timeframe.
I was just reading the other day about Kangbashi, the “ghost city” of Ordos, China. It was built in five years flat for a million people. It’s interesting to me that they’re willing to work at this speed in an attempt to catch up, even regardless of the consequences.
 [Image: A rendering of New Songdo City, courtesy of Kohn Peterson Fox].
[Image: A rendering of New Songdo City, courtesy of Kohn Peterson Fox]. BLDGBLOG: I’d like to discuss the idea of the “instant city” more generally. It’s an evergreen vision, in many ways, and an ideologically promiscuous one, appealing both to the 1960s architectural avant-gardes and to the overseas forward-operating bases of military planners. In your own work, you’ve covered things like the “City in a Box,” New Songdo City, and Russia’s “silicon forest” where cities are basically treated as products that you can buy—like customizing a BMW off a website and then hitting the purchase button. Where is this sort of instant urbanism going, and who or what is driving it?
Lindsay: The thread I see going through the book and the work I’ve been doing for Fast Company is the notion that the people who are planning cities today, and who have really gotten interested in urbanism over the last few years, are people who are neither architects nor planners. The city is experiencing a white-hot moment, and this is converging from a bunch of different areas.
You have the whole camp coming out of Richard Florida’s work, for example, who have gone through the economic effects of cities and the cultural spillover of knowledge and training—basically, the notion that cities are engines of creativity and engines of ideas and job skills. Harvard’s Edward Glaeser is deservedly enjoying his moment in the sun for his academic work around these issues. To him, the key economic actor of the future is the city.
Then you have the technology companies who have been piling in, led by IBM. This is what really led to the resurrection of the “smart city” a couple years ago, which is the notion that, coupled with the "internet of things"—assuming we reach a point of ubiquitous sensors and constant data flows—the city becomes the next computing paradigm. This has been discussed academically for decades, but now it might actually happen—or at least there’s a lot of money and corporate support behind it.
Then you get to the notion, again, of infrastructure—of Kasarda, of the aerotropolis, and of people who are building cities as competitive weapons.
Some of the most interesting things I like writing about are places like New Songdo City. Songdo is billed today as a smart, green aerotropolis, but it was invented by the Korean government at the insistence of the International Monetary Fund following the 1997-98 financial crisis, when the IMF bailed out Korea to the tune of $58 billion—which seems like nothing now. The IMF insisted the country open itself up to foreign direct investment. So its leaders decided to build a city for foreigners, and that led to finding an American—Stan Gale and his partners—to build a whole city from scratch off the coast of Korea. It was basically willed into existence by the necessity of paying back the IMF; that’s why Songdo was born.
Or there are the smart cities being planned. Masdar, for example, is supposed to be a smart eco-city. Masdar basically exists to be an incubator and an R&D park so that Abu Dhabi can dominate clean-tech technology. Again, this is basically the city as an economic weapon, not a utopian vision.
I find the people drawn to these projects equally fascinating. For example, Stan Gale is your classic story of American real-estate development. He’s a third-generation developer who got his own start in Orange County in the 1980s, and he witnessed the master planning and the financialization of real estate that began there; he then worked in New Jersey in the 1990s, where the market evolved into edge cities; and now here he is working at the global scale, trying to convince more Chinese mayors to help him build cities for them. He’s got a whole consortium of companies, like Cisco and United Technology Corporation—which, incidentally, builds more pieces of the city than I think anyone really knows. Otis Elevators, fuel-cells—all these things that you need for a project being built at the city scale.
Someone else I find equally fascinating is Paul Romer, the economist who’s pitching the idea of the charter city. I’d like to think he’ll win the Nobel Prize for the work he did in the 1990s on what’s been called New Growth theory, which described increasing returns to scale. Paul basically decided that the best way to raise people out of poverty—the best instrument—is to build a city from scratch and use it as a tool for developing skills, trade and everything else. And it appears that he’s actually now found a country willing to let him do it, in Honduras. This is a man who has absolutely no urban planning background. Urbanism to him is secondary—he cares, but he’ll leave it to the experts. The urbanism itself is not paramount to him.
It’s interesting to me that these outside elements—whether it’s a technology company or an economist or a developer—feel like the architecture and the urban planning is just—you know, we can get experts to do that for us. And it’ll be great. Architects like Kohn Peterson Fox, who are responsible for Songdo, rather than build a perfect city from scratch, basically borrow the best pieces of every city they can find to create a new city. And, you know, having been there a couple of times, I feel like it may actually work; I don’t know what the completed city will be like, but I feel like it’s working. Gale uses the phrase “city in a box,” which you mentioned, but they’re also saying things like “we’ve cracked the code of urbanism”—which is a hell of a statement to make. To think you’ve solved 9,000 years of urban practice and that you can just move on is quite dramatic.
So those are some of the things I find particularly interesting: that the city has become this nexus of interests for so many people, only it’s being made or stimulated by people who aren’t architects or urban planners.
 [Image: Le Corbusier's infamous Plan Voisin, meant to replace the heart of Paris, France].
[Image: Le Corbusier's infamous Plan Voisin, meant to replace the heart of Paris, France].BLDGBLOG: It’s easy to see how all this can sound quite technocratic and dystopian—which makes it all the more interesting that you open the book with an unexpected pair of quotations. One is from Le Corbusier, the other from novelist J.G. Ballard. To anyone familiar with Ballard’s work, in particular, I might say, this seems like a strangely subversive gesture against the book's own premise; it's like opening a golf course community and saying you were inspired by Super-Cannes. Why did you choose these quotations, and what effect were you hoping they would have?
Lindsay: I’m so glad you brought that up. I’ve been curious what people would make of it. What I love about Ballard is the kind of dark irony of his work, which is something I find in Koolhaas’s writing as well. They know the future is slick and disposable, and they revel in modernity’s contradictions. They know how dark globalization’s undercurrents are, but go on despite—or even because of—them. The book reviewers who said the aerotropolis had “forgotten” a soul completely missed the point—these cities never had souls to begin with. That’s why I find them fascinating!
The Ballard and Le Corbusier quotes should be read as a flashing red light, signaling to the reader: Caution: Unreliable Narrator Ahead. You’ve been warned. Especially that Le Corbusier quote: anyone who knows anything about urbanism who encounters that quote should immediately have their guard up—which was my intention all along.
Thanks again to Greg Lindsay for having this conversation—including the second half, which you can read over at Work in Progress—and to Stephen Weil for all his help in setting this up.
Finally, I hope to see some of you in Los Angeles at the A+D Museum on April 5th, when Greg Lindsay and I will pick up this conversation in person. The event is free and open to the public, and it kicks off at 6pm.
Monday, May 10. 2010
Uneven Geographies: Art and Globalization
Via e-flux
-----

![]()
Eduardo Abaroa
Proposal: We Just Need a Larger World, 2009 (detail)
Courtesy the Artist & kurimanzutto gallery, Mexico City
Uneven Geographies:
Art and Globalization
8 May – 4 July 2010
Nottingham Contemporary
Weekday Cross
Nottingham NG1 2GB
UK
info@nottinghamcontemporary.org
http://www.nottinghamcontemporary.org ![]()
Éduardo Abaroa (Mexico City), Yto Barrada (Tangiers), Ursula Biemann (Zurich), Bureau d'Études (Paris), Öyvind Fahlström, (Rio de Janeiro, Stockholm & New York), Goldin + Senneby (Stockholm), Mark Lombardi (New York), Steve McQueen (Amsterdam & London), Cildo Meireles (Rio de Janeiro), George Osodi (Lagos & London), Bruno Serralongue (Paris), Mladen Stilinović (Zagreb), Yang Zhenzhong (Shanghai)
Curated by TJ Demos and Alex Farquharson (Director, Nottingham Contemporary)
Uneven Geographies focuses on projects by artists concerned variously with visualising the transnational mobility of capital, goods and people in today's global networks. Its point of departure is the assumption that the opaque and labyrinthine workings of worldwide economies tend to frustrate attempts to represent the historic conditions and expanding geographies that define current forms of globalization. Artists have consequently turned to the invention of innovative ways of imaging and narrating, analysing and reconceptualizing the processes and relations of globalization - whereby geopoetics mediates geopolitics.
Without returning to an imaginary lost language of objectivity, these artists' practices mobilize experimental forms of transnationalism—whether in regards to labour, migration, or resource allocation—via active and creative re-stagings by which the underlying relations of profit and exploitation become legible and are imaginatively reconfigured. These strategies creatively re-animate the novelistic and poetic, the cartographic and the documentary, the performative and the ludic, which connect to global processes situated in relation to varied geographies, including Mexico, the Congo, Morocco, Central Asia, the Bahamas and Mumbai. In the case of Fahlstrom—here the exhibition's historical forebear—and Lombardi, networks are tracked, rhizomatically, around the globe in diverse flows of capital and relations of power. With the photographic and video-based projects of Barrada and Biemann, passages of migration are imaged with ambivalence, evoking both the disenfranchisement of statelessness and its empowering potential. Whereas McQueen invests the imagery of Sub-Saharan manual labour with perceptual affect and literary allusion, contesting documentary legibility yet connecting current operations to the history of colonialism, Goldin + Senneby reveal how the conditions of post-representation serve as well to cloak unregulated economic power today.
These far-reaching engagements with the creative imaging of the cultural geographies of globalisation will be extended further through its public programme, in partnership with University of Nottingham and Nottingham Trent University. The programme include Lars Bang Larsen on Öyvind Fahlström, a short residency by Ursula Biemann, Renzo Martens and Alfredo Cramerotti on Episode III – "Enjoy Poverty", John Tomlinson on the acceleration of capitalism, and a keynote lecture by Saskia Sassen. The exhibition opens with a one-day conference, The Geopolitical Turn: Art and the Contest of Globalization featuring Cramerotti (author, Aesthetic Journalism), Angus Cameron (co-author, The Imagined Economies of Globalization and emissary of Goldin + Senneby), Mark Fisher (author, Capitalist Realism), geographer Alex Vasudevan, Sara Motta (Co-Director of The Centre for the Study of Global and Social Justice at The University of Nottingham), participating artists Biemann, Dario Azzellini and Oliver Ressler, Bureau d'Études and George Osodi and the exhibition's curators. All events are free but booking is essential. See our website for full dates: http://www.nottinghamcontemporary.org
Tuesday, September 29. 2009
Towards a new architect: an interview with Carlo Ratti
I’ve just finished working with Carlo Ratti and various cohorts on a great little project, which I hope might see the light of day here before too long. In the meantime, I thought I’d post this discussion I had with Carlo late last year, which was recently published in Architectural Review Australia. We met at the Metropolis Congress in Sydney, where Signor Ratti had just given a presentation on his work at the MIT SENSEable City Lab, an outfit whose work I admire hugely, working as they do across many of my interests: interactive architecture, urban informatics, responsive envronments, multidisciplinary design and other implications of real-time networked pervasive information systems for the city.
(Incidentally, the interview was also recently published on the new-ish Australian Design Review website - which amalgamates AR with its sister publication (Inside) - and which is rather nice and proving more than a little useful. Kudos to Andrew Mackenzie and Mat Ward for steering that through so well.)
To the discussion/article ...
Carlo Ratti and his colleagues at the SENSEable City Lab at MIT are doing as much as anyone to define a future of architecture. Ratti and I meet up at the Metropolis Congress in Sydney, where he has delivered a keynote on his projects, sandwiched between Saskia Sassen and Kathy Pain. Ratti’s presentation provided a strong counterpoint to Sassen’s impassioned yet personal world view, and Pain’s apparently analytical yet ultimately superficial ranking of cities. The work of his team was, in contrast, suffused with data emerging from the aggregate of millions of tiny signals. Yet it was often realised in lustrous visualisations that attempted the alchemy of transmuting data into information into knowledge, while shifting effortlessly from physical to digital to physical.
Ratti, an architect and civil engineer by training, has ended up creating new urban forms from mobile phone signals, the movement of bikes and digitally-controlled jets of water. My own work, leading on ‘urban informatics’ for Arup in Australasia, is also getting our business into unlikely places, at both ends of the ‘design food chain’ and hovering around this intersection between physical and digital. The name ‘informatics’ will change, surely, just as talkies became movies, and Ratti talks instead of a “living architecture”, “liberated pixels” and “physical plus”. Yet we, and many others worldwide now, are all wrestling with the promise of digital activity thoroughly permeating urban fabric.
Ratti is a tall, slender and slightly gangling arc of good-natured exuberance. He in no way belies Italian caricatures by gesticulating with a flourish as he talks, carving the air around him into sinuous forms, sweeping his hands to indicate progressive movements. Sitting in the culturally arid hub of Darling Harbour, we talk for a couple of hours, exploring the implications of this emerging field of design work, and how it may change the nature of both architecture, and also cities and buildings themselves.
Just as with Ratti, his projects emerge from an intrinsically multidisciplinary environment. The Water Pavilion, for the Zaragoza Expo, was produced by a team of engineers, architects, sociologists and physicists, and built by Siemens. The presence of the social science disciplines is particularly interesting, enabling a focus on user behaviour in far more detail than is often the case with the built environment. As Ratti puts it, designing public spaces that are infused with informational activity means absolutely addressing “a new type of space and a new type of (augmented) physical body”, which is why he sees sociologists as so important, to help quantify some of these changes, and to monitor and understand them.
I reflect that in industrial design and web design in particular it is far more common to have that sort of user research-led approach, but that it doesn’t often happen in architecture or urban design. Though some architects have frequently indicated the possibilities of introducing industrial design techniques into architecture, others respond that buildings are generally one-offs, that “each building is a prototype”, and not mass produced as cars are (leaving aside the so far largely unrealised promise of prefab).
Ratti agrees that approaches such as ethnographic research or user-centred design, don’t occur within architecture often. He suggests that the focus on the user’s behaviour pervading the design process (to the extent that product designers like Naoto Fukasawa can say, “Design is dissolving in behaviour”) is largely due to the rapid pace of technological change in product design, whether industrial or informational (or the emerging hybrid of the two). But, as he explains, “Traditionally architecture is much more static. Now, because of all the new technology in the city, you might require this new type of responsive city – and building that comes from other disciplines too, including industrial design.”
Architecture can be very slow-moving by nature, partly as many basic conditions don’t change that much – such as the structural loads on buildings from wind or snow – and that materials tend to have a slow pace of change, with many years in between the introduction of concrete and that of ETFE, for instance. Whereas the world of consumer electronics, product design or, more obviously, online social software, can change radically almost week to week.
Ratti notes that behaviour around these products flexes accordingly too, in a symbiotic relationship, and this must be understood in detail. At MIT, he benefits from a highly multidisciplinary environment, despite the silos universities can sometimes wrangle themselves into. Technological innovation can be situated in an environment where there can be “a dialogue between the technology side and the behavioural side – an interplay between the social and the technology”, as he puts it.
With the SmartBiking project – in the context of a Copenhagen where 30 to 40 percent of all trips are already undertaken by bicycle – attempts to further promote the use of bikes need to genuinely develop new thinking over and above the pervasive provision of bike lanes. By looking at powerful connective tissue of social software networks, Ratti’s team – working with William J. Mitchell and others at MIT – is developing what they call “spatial smart wheels” that harvest energy when the rider brakes, within the context of a city-wide carbon trading scheme. Their sensor-enabled bikes connect briefly to other cyclists as they ride by, and then enable Facebook to play back the patterns of who passed who in the street that day.
This is hardly the traditional work of the architect, yet this sense of working with a layer of soft infrastructure, overlaid onto the hard infrastructure of the city, is a theme common to this work. One thing that I consistently get asked by clients when I talk them through these kinds of changes is, “Yeah, but how will it change the physical form of cities? How will the cities look different?” I sometimes respond by referencing those other bike-sharing schemes in Barcelona, Paris, Lyon et al and illustrating how these are really informational services; soft infrastructure coordinated by informatics, and laid over the existing fabric of the city. Aside from hubs for the bikes, there are very few physical changes to the cities. Yet these systems have radically changed the sense of mobility in their cities, utterly changing the way the city feels.
Ratti agrees, seeing that digital activity is a layer in interface with the city. It’s not a separate virtual space, as some seem to think, but it’s augmenting our physical space. As he points out, we’re hardly going to change or destroy all these existing buildings and spaces anytime soon – urban form just doesn’t change that quickly, but the profound changes in the way cities feel and function may be in this internet-enabled informational layer.
And yet, Ratti is an architect (in practice with his Turin-based firm carlo ratti associati – Walter Nicolino & Carlo Ratti) and he is still drawn to creating new forms and shaping physical space. The Water Pavilion suggests a newly fluid, reconfigurable architecture, although with exterior walls comprising jets of water. By controlling these jets – broadly, with a similar principle to ink-jet printers – words and shapes can be formed in the ‘walls’ and the walls themselves can appear and disappear from one second to another, such that the form of the building responds to people approaching it, shifting climactic conditions and other patterns of behaviour. In this sense, it’s beyond simply responsive architecture, and more genuinely interactive. Ratti describes these projects as exploring a new form of skin, which he sees has potential to be “reactive, responsive, more living”. He’s proud of how kids in particular responded to it, fluidly altering the physical space. “More Spacebook than Facebook,” he says, smiling.
For the New York Talk Exchange (NYTE) project – a visualisation of global traffic over AT&T’s network, zooming from country to city to borough, to construct a kind of real-time census – the team included an urban designer, information designer, sociologist, exhibition designer, architecture student and a couple of advisers on the content itself. The latter was to advise the project on the content contained within the data, almost to avoid the team becoming seduced by the visualisation possibilities. Ratti believes this project begins to enable an understanding of the structure of cities from the fine-grain (even though the NYTE project could still be criticised for its lack of context, poor Dr Kathy Pain following Ratti’s presentation at Metropolis simply had no way of responding to this detail of data; the GAWC index of cities begins to look very old-fashioned as a result).
Real-Time Rome provided another compelling example of these urban patterns, drawn from the aggregated mobile phone signals over the course of three days surrounding the 2006 World Cup Final between Italy and France. Using AI techniques to infer pedestrian activity from the signals, it’s clear in which bits of the city the fans gathered to watch the game, where the victorious Italian team paraded the trophy through the streets, and how this use of the city changed in response to events during or after the game.
We then talk of how ‘dataviz’ like NYTE and Real-Time Rome may have a physical existence too, a presence in the city. Ratti certainly sees the possibilities in extending these information layers across mobile phones and web, onto the fabric of our streets and buildings, using LEDs and other technologies to enable quite fluid forms of display. He likes the idea of these clouds of pixels deployed around the street, the idea of the ‘liberated pixel’ not contained within the overbearing rectangular form of ‘the big screen’.
Yet beyond installations, Ratti suggests that these kinds of real-time systems may actually radically reorient services such as transport, which are still wedded to the somewhat blunt Industrial Age artefacts of timetables and prescribed routes. Put simply, he says the bus could follow us, rather than us following the bus.
As with the internet itself, this work comes from somewhere, and also has a history within architecture. Perhaps our roots are showing, but in terms of antecedents, I suggest (Brits) Archigram, Reyner Banham and Cedric Price, whereas Ratti references (Italians) Archizoom and Superstudio. Yet for Ratti, Buckminster Fuller’s concept of “comprehensive anticipatory design” provided most inspiration.
His team, he says, are trying to define possible future urban conditions, which are articulated through design and then generate research responses. I suggest this approach – design and publish – is also close to Archigram and Superstudio, and Ratti particularly responds to the Superstudio comparison. He recalls their technique of creating radical visions of extreme or absurd conditions. In this sense, he thinks, they were not anticipatory, instead extrapolating a present condition to absurdity, as with the Continuous Monument or its heritage-parodying proposal for flooding Florence.
With these intense exaggerations of form and city, they were commentaries on contemporary conditions, almost as a science fiction writer will almost inevitably write about today when depicting visions of tomorrow. Ratti is clearly drawn by this idea of exaggeration and extrapolation, almost to the point of absurd reductions, and I wonder whether there’s a link with Real-Time Rome, where instead of addressing the vast richness of all of city life, we use only mobile phone data to tell a story about the city. It’s a slice through the city on only one axis, which is a slightly absurd thing to do. Yet it still enables interpretation. It still speaks of now.
Ratti agrees, but then outlines the possibility of accreting layers of such data – in partnership with the buses, the taxis, the wider city – to create a platform for exploring the city through data. In this, his aspirations are indeed closer to Fuller than Superstudio, as it becomes a form of anticipatory design. He doesn’t think you can show the city of the future as it will be, but you can see real-time information along one slice, one axis, and this enables us to anticipate a future city where perhaps the majority of the urban activity will generate impossible swathes of real-time data.
I wonder whether we can almost think of information as a material in a sense, in terms of it having its own capabilities, qualities and performance criteria. Ratti responds by saying that there’s no doubt that the digital revolution has genuinely changed the way we do things, the way we live, the way we interact and talk with others. And rapidly too, as if 1993 was 50 years ago in “internet years”. He thinks there are similar conditions here as those that Le Corbusier reflected upon in 1929, when he saw a machine civilisation looking for and finding its architectural expression. Clearly Ratti believes that this age too has now begun its search.
So these cities of the future are still made of concrete, but also of transient slivers of silicon and amorphous clouds of wireless activity. Atoms and bits. The great promise of informatics – or whatever we end up calling it – is that the fabric of the city is once again malleable, responsive and can adapt through learning from layered patterns of behaviour. Perhaps we don’t call it informatics, but architecture and engineering, just a new form of both crafts. Yet these developments pose radical changes, from the point of view of skills, processes, business models and purpose, and Ratti and his crew of collaborators are indicating one possible future for our work. He concludes by tentatively suggesting, “It’s almost redefining, I believe, what being an architect is.”
Bonus postscript: My sketch of the new multidisciplinary architectural practice. Of course in practice I'd expect all these roles to overlap, blurring into each other constructively:
Related Links:
fabric | rblg
This blog is the survey website of fabric | ch - studio for architecture, interaction and research.
We curate and reblog articles, researches, writings, exhibitions and projects that we notice and find interesting during our everyday practice and readings.
Most articles concern the intertwined fields of architecture, territory, art, interaction design, thinking and science. From time to time, we also publish documentation about our own work and research, immersed among these related resources and inspirations.
This website is used by fabric | ch as archive, references and resources. It is shared with all those interested in the same topics as we are, in the hope that they will also find valuable references and content in it.
Quicksearch
Categories
Calendar
|
|
December '25 | |||||
| Mon | Tue | Wed | Thu | Fri | Sat | Sun |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 | ||||
